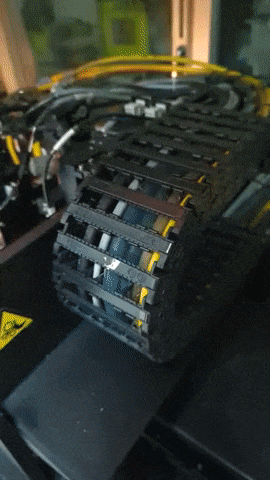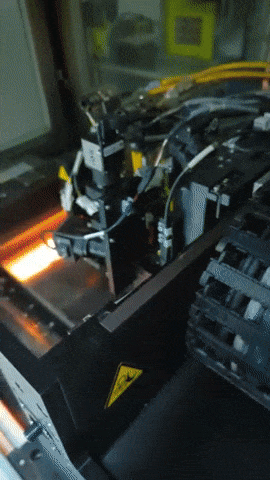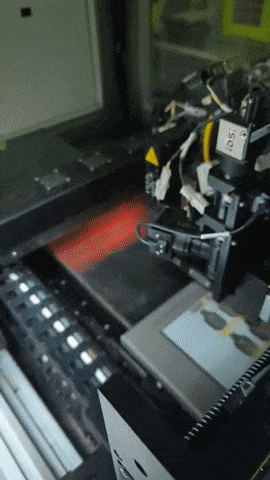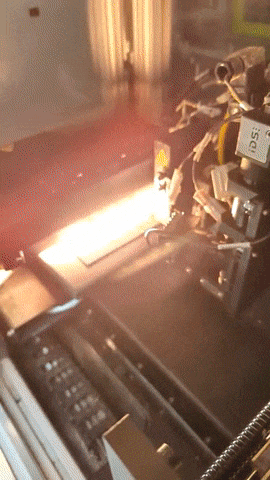
Printed electronics involves 3D printing a variety of electrically active materials such as metals or carbon-doped polymers to form devices like transistors, capacitors and resistors, plus the electrical connectors linking them together.
“Printed and flexible EEE components are fast rewriting the future of electronics,” explains ESA Internal Research Fellow Rita Palumbo, overseeing a new working group on the topic. “So we are looking into how space could benefit from this step change.”
Dr Palumbo’s multidisciplinary working group spans multiple ESA sites and brings together experts from different areas of expertise, such as materials, components, antennas and microwave payloads, spanning four ESA Directorates – Earth Observation; Human and Robotic Engineering; Technology, Engineering and Quality; and Telecommunications and Integrated Applications – with the goal of creating a shared roadmap for the introduction of printed electronics to the space sector.