Copernical Team
Blue Origin unveils "Blue Alchemist" a technology that turns Moon dust into solar cells
 Jeff Bezos' spaceflight company Blue Origin revealed on February 10, 2023, in their blog that since 2021 they have been developing an in-situ resource utilization (ISRU) technology called "Blue Alchemist" a solar cell and electricity transmission wire prototype by using a material "chemically and mineralogically equivalent" to lunar regolith.
"We can make power systems on the moon directly
Jeff Bezos' spaceflight company Blue Origin revealed on February 10, 2023, in their blog that since 2021 they have been developing an in-situ resource utilization (ISRU) technology called "Blue Alchemist" a solar cell and electricity transmission wire prototype by using a material "chemically and mineralogically equivalent" to lunar regolith.
"We can make power systems on the moon directly Four classes of planetary systems
 Astronomers have long been aware that planetary systems are not necessarily structured like our solar system. Researchers from the Universities of Bern and Geneva, as well as from the National Centre of Competence in Research PlanetS, have now shown for the first time that there are in fact four types of planetary systems.
In our solar system, everything seems to be in order: The smaller r
Astronomers have long been aware that planetary systems are not necessarily structured like our solar system. Researchers from the Universities of Bern and Geneva, as well as from the National Centre of Competence in Research PlanetS, have now shown for the first time that there are in fact four types of planetary systems.
In our solar system, everything seems to be in order: The smaller r Team Aims To Find Earth 2.0
 Are there other Earth-like planets? Is there extraterrestrial life? In the quest to find planets that orbit stars other than the sun, "Earth 2.0" is the Holy Grail. Earth 2.0 is a planet similar enough to Earth to enable the existence of life as we know it. It would be the right temperature for liquid water, and it would orbit a star with a steady supply of light. Ideally, it would be close enou
Are there other Earth-like planets? Is there extraterrestrial life? In the quest to find planets that orbit stars other than the sun, "Earth 2.0" is the Holy Grail. Earth 2.0 is a planet similar enough to Earth to enable the existence of life as we know it. It would be the right temperature for liquid water, and it would orbit a star with a steady supply of light. Ideally, it would be close enou NASA's IMAP spacecraft completes mission critical design review, moves closer to 2025 launch
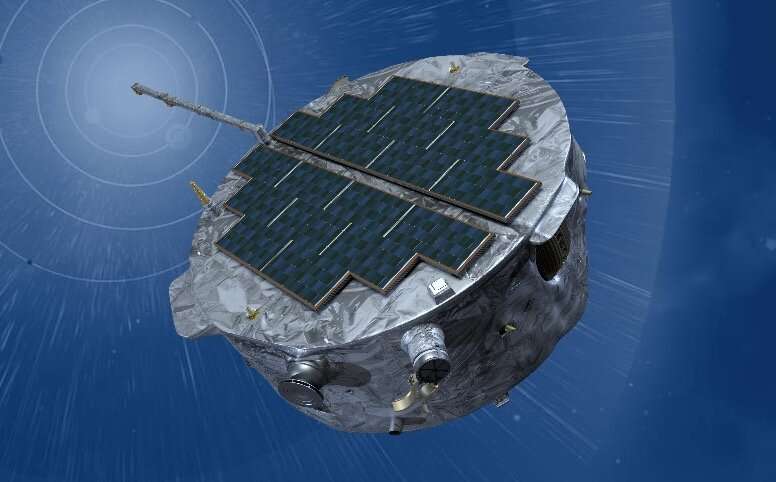

NASA's Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe (IMAP) spacecraft has completed the Mission Critical Design Review and is on track to meet its scheduled 2025 launch. Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) is managing the payload office, providing the scientific instrument Compact Dual Ion Composition Experiment (CoDICE) and is participating on other instrument teams for the mission, which will study the interaction between the solar wind and the interstellar medium as well as the fundamental processes of particle acceleration in space.
The roar and crackle of Artemis 1
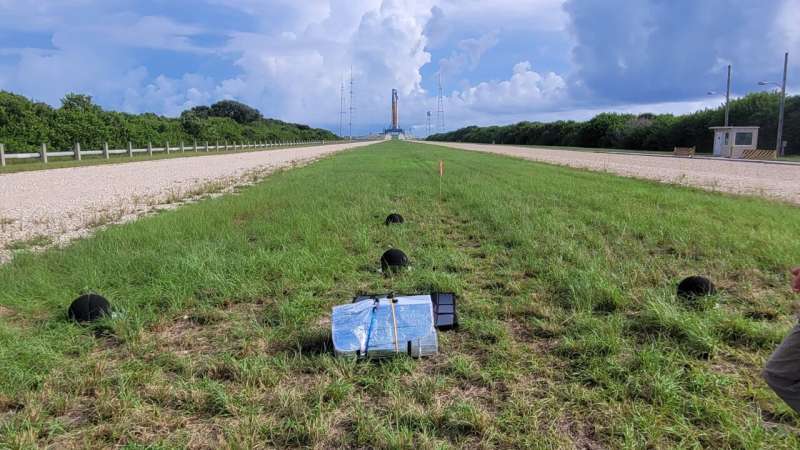

When the Artemis 1 mission was launched by NASA's Space Launch System, SLS, in November, it became the world's most powerful rocket, exceeding the thrust of the previous record holder, Saturn, by 13%. With liftoff came a loud roar heard miles away.
In JASA Express Letters, researchers from Brigham Young University and Rollins College in Florida reported noise measurements during the launch at different locations around Kennedy Space Center.
The data collected can be used to validate existing noise prediction models, which are needed to protect equipment as well as the surrounding environment and community. These data will be useful as more powerful lift vehicles, including the SLS series, are developed.
"We hope these early results will help prevent the spread of possible misinformation, as happened with the Saturn 5," author Kent Gee said. "Numerous websites and discussion forums suggested sound levels that were far too high, with inaccurate reports of the Saturn 5's sound waves melting concrete and causing grass fires.
Minuteman III test launch showcases readiness of U.S. nuclear force's safe, effective deterrent
 A team of Air Force Global Strike Command Airmen launched an unarmed Minuteman III intercontinental ballistic missile equipped with a test reentry vehicle at 11:01 p.m. Pacific Time Feb. 9 from Vandenberg Space Force Base, California.
This test launch is part of routine and periodic activities intended to demonstrate that the United States' nuclear deterrent is safe, secure, reliable and e
A team of Air Force Global Strike Command Airmen launched an unarmed Minuteman III intercontinental ballistic missile equipped with a test reentry vehicle at 11:01 p.m. Pacific Time Feb. 9 from Vandenberg Space Force Base, California.
This test launch is part of routine and periodic activities intended to demonstrate that the United States' nuclear deterrent is safe, secure, reliable and e Tracking ocean microplastics from space
 New information about an emerging technique that could track microplastics from space has been uncovered by researchers at the University of Michigan. It turns out that satellites are best at spotting soapy or oily residue, and microplastics appear to tag along with that residue.
Microplastics-tiny flecks that can ride ocean currents hundreds or thousands of miles from their point of entry
New information about an emerging technique that could track microplastics from space has been uncovered by researchers at the University of Michigan. It turns out that satellites are best at spotting soapy or oily residue, and microplastics appear to tag along with that residue.
Microplastics-tiny flecks that can ride ocean currents hundreds or thousands of miles from their point of entry FCC greenlights Amazon's Project Kuiper to deploy 3,236 satellites in LEO
 The Federal Communications Commission's (FCC) International Bureau approved Amazon on February 8 to deploy and operate their 3,236 low-Earth orbit (LEO) satellites, called "Project Kuiper," for broadband service using Ka-band radio frequencies.
The approval comes after satisfying requirements for orbital-debris mitigation, collision risk, and coordination with other satellite systems, re-e
The Federal Communications Commission's (FCC) International Bureau approved Amazon on February 8 to deploy and operate their 3,236 low-Earth orbit (LEO) satellites, called "Project Kuiper," for broadband service using Ka-band radio frequencies.
The approval comes after satisfying requirements for orbital-debris mitigation, collision risk, and coordination with other satellite systems, re-e Rumors swirl about balloons, UFOs as officials stay mum

Media invitation: View Euclid spacecraft in Cannes before launch

Journalists are cordially invited to view Euclid, ESA’s ambitious mission to explore the dark Universe, in Cannes, France, on 21 February 2023.
Media will be given the rare opportunity to see the spacecraft in the cleanroom of Thales Alenia Space (TAS), prior to shipment for its launch from Cape Canaveral, Florida, USA in July 2023.