Copernical Team
NASA Moon capsule Orion due to splash down after record-setting voyage
 After making a close pass at the Moon and venturing further into space than any previous habitable spacecraft, NASA's Orion capsule is due to splash down Sunday in the final test of a high-stakes mission called Artemis.
As it hurtles into Earth's atmosphere at a speed of 25,000 miles (40,000 kilometers) per hour, the gumdrop-shaped traveler will have to withstand a temperature of 2,800 degre
After making a close pass at the Moon and venturing further into space than any previous habitable spacecraft, NASA's Orion capsule is due to splash down Sunday in the final test of a high-stakes mission called Artemis.
As it hurtles into Earth's atmosphere at a speed of 25,000 miles (40,000 kilometers) per hour, the gumdrop-shaped traveler will have to withstand a temperature of 2,800 degre Orion splashdown
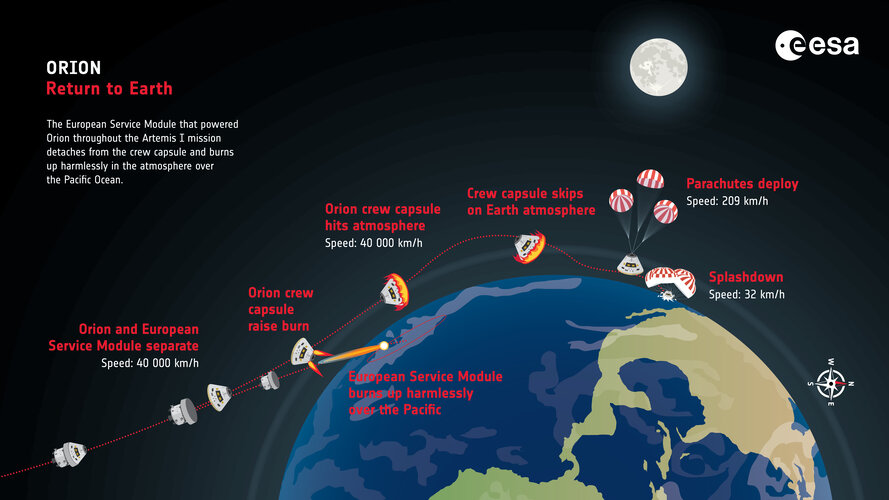 Image:
Orion splashdown
Image:
Orion splashdown NASA spacecraft will soon enter Earth's atmosphere at nearly 25,000 mph. What will happen next?

Sunday at around 10:40 a.m. MT, NASA's Orion spacecraft will splash down in the Pacific Ocean after its several week-long journey to the moon and back. Space buffs can tune into NASA's livestream to witness some extreme physics—what will be the last leg of the historic Artemis 1 mission, which launched from Florida Nov. 15.
The numbers are mind-boggling: The Orion capsule will hit Earth's atmosphere flying at speeds of almost 25,000 mph (or about 11 kilometers per second) and experience temperatures nearing 5,000 degrees Fahrenheit in the process.
Iain Boyd is a professor in the Ann and H.J. Smead Department of Aerospace Engineering Sciences who has spent his career studying hypersonics, or vehicles that travel far faster than the speed of sound. He also leads a $15 million NASA institute called the Advanced Computational Center for Entry System Simulation (ACCESS). This effort investigates new ways to protect spacecraft as they undergo the extremes of entering atmospheres on Earth, Mars and beyond.
Looking back from beyond the moon: How views from space have changed the way we see Earth

A photograph taken by NASA's Orion spacecraft has given us a new perspective on our home planet.
The snap was taken during the Artemis I mission, which sent an uncrewed vehicle on a journey around the Moon and back in preparation for astronauts' planned lunar return in 2025.
We get pictures of Earth every day from satellites and the International Space Station. But there's something different about seeing ourselves from the other side of the Moon.
How does this image compare to other iconic views of Earth from the outside?
Earthrise
In December 1968, three astronauts were orbiting the Moon to test systems in preparation for the Apollo 11 landing. When they saw Earth rise over the lunar horizon, they knew this was something special. The crew scrambled to find color film in time to capture it.
Photographer Galen Rowell called the resulting image "the most influential environmental photograph ever taken.
Christmas challenge: find mystery asteroid

Deep-space optical communication demonstration project forges ahead

Researchers report new results from the NASA Deep Space Optical Communications (DSOC) technology demonstration project, which develops and tests new advanced laser sources for deep-space optical communication. The ability to perform free-space optical communication throughout the solar system would go beyond the capabilities of the radio communication systems used now and provide the bandwidth necessary for future space missions to transmit large amounts of data, including high-definition images and video.
The demonstration system consists of a flight laser transceiver, a ground laser transmitter and a ground laser receiver. The downlink transmitter has been installed on the Psyche spacecraft, which will travel to a unique metal asteroid also called Psyche, which orbits the sun between Mars and Jupiter.
Malcolm. W. Wright, from the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology, will present the functional and environmental test results of the DSOC downlink flight laser transmitter assembly and ground uplink transmitter assembly at the Optica Laser Congress, 11-15 December 2022.
SpaceX gives rival's internet satellites ride to orbit
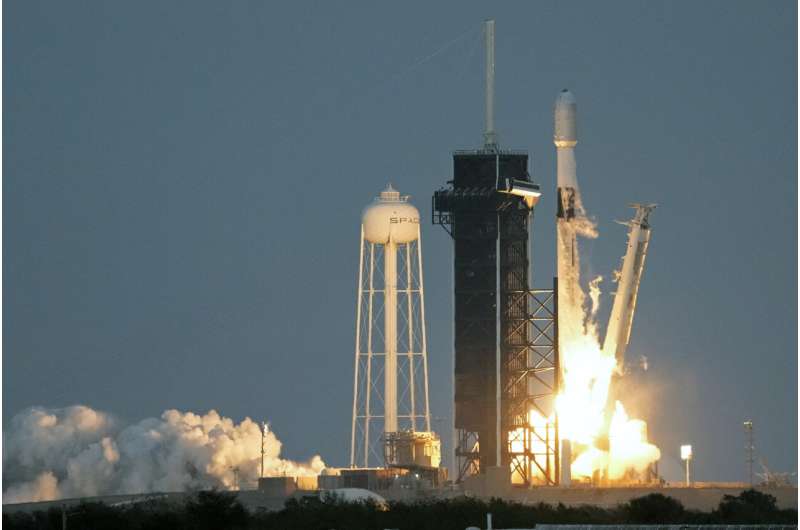

SpaceX launched internet satellites for a competitor Thursday, stepping in to help after the London-based OneWeb company halted its flights with Russia over the invasion of Ukraine.
The Falcon rocket blasted off at sunset with 40 mini satellites bound for polar orbit. They will expand OneWeb's constellation to just over 500, nearly 80% of the planned total of about 630 satellites.
Elon Musk's SpaceX has more than 3,200 Starlink satellites in orbit, providing high-speed, broadband internet to remote corners of the world.
Earth from Space: Fucino, Italy
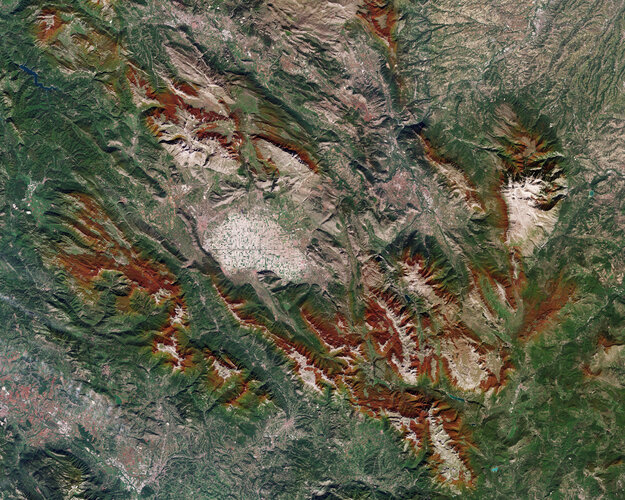

Tucked away in the Fucino Valley, in central Italy, lies the Fucino Space Centre, where Telespazio will manage the early orbit activities of the Meteosat Third Generation Imager, set to launch on 13 December from Europe’s Spaceport in French Guiana.
Evaluating a Possible Drill Location
 The weekend drive went well and Curiosity is back on top of the marker band, investigating some intriguing rippled bedrock. We're assessing whether we want to drill at this location, based on what we see in the chemistry data.
So today's two-sol plan is devoted to collecting data from APXS and MAHLI (supplemented by ChemCam and Mastcam), to evaluate the bedrock in our workspace, as seen in
The weekend drive went well and Curiosity is back on top of the marker band, investigating some intriguing rippled bedrock. We're assessing whether we want to drill at this location, based on what we see in the chemistry data.
So today's two-sol plan is devoted to collecting data from APXS and MAHLI (supplemented by ChemCam and Mastcam), to evaluate the bedrock in our workspace, as seen in Phantoms return from beyond the Moon with valuable data on cosmic radiation doses
 Together with the Orion spacecraft of the Artemis I mission, as part of the MARE experiment, two human phantoms equipped with numerous cosmic rays detectors are to land on Earth. The information gathered by the detectors will for the first time verify the knowledge, crucial for the presence of humans in deep space, of the effects of cosmic rays on the health of the astronauts who are to live and
Together with the Orion spacecraft of the Artemis I mission, as part of the MARE experiment, two human phantoms equipped with numerous cosmic rays detectors are to land on Earth. The information gathered by the detectors will for the first time verify the knowledge, crucial for the presence of humans in deep space, of the effects of cosmic rays on the health of the astronauts who are to live and