Equatorial Launch Australia Unveils Innovative ASC Advanced Launch Pad Designs
Tuesday, 19 December 2023 03:47 Equatorial Launch Australia (ELA) has announced a significant breakthrough in launch pad technology with the completion of its Arnhem Space Centre Advanced Launch Pad (ASCALP) designs. This development marks a pivotal moment in the NewSpace sector, known for its innovative and rapidly evolving approach to space exploration and commercialization.
The ASCALP, hailed as the most advanced laun
Equatorial Launch Australia (ELA) has announced a significant breakthrough in launch pad technology with the completion of its Arnhem Space Centre Advanced Launch Pad (ASCALP) designs. This development marks a pivotal moment in the NewSpace sector, known for its innovative and rapidly evolving approach to space exploration and commercialization.
The ASCALP, hailed as the most advanced laun NASA's Tech Demo Streams First Video From Deep Space via Laser
Tuesday, 19 December 2023 03:47 NASA's Deep Space Optical Communications experiment beamed an ultra-high definition streaming video on Dec. 11 from a record-setting 19 million miles away (31 million kilometers, or about 80 times the Earth-Moon distance). The milestone is part of a NASA technology demonstration aimed at streaming very high-bandwidth video and other data from deep space - enabling future human missions beyond Ea
NASA's Deep Space Optical Communications experiment beamed an ultra-high definition streaming video on Dec. 11 from a record-setting 19 million miles away (31 million kilometers, or about 80 times the Earth-Moon distance). The milestone is part of a NASA technology demonstration aimed at streaming very high-bandwidth video and other data from deep space - enabling future human missions beyond Ea Quantum Leap in secure communication: Teleporting images using light
Tuesday, 19 December 2023 03:47 In a groundbreaking study published in Nature Communications, an international team from Wits University and ICFO- The Institute of Photonic Sciences has unveiled a novel technique for transporting patterns of light, akin to image teleportation, across a network without the physical transmission of the image itself. This research not only challenges our conventional understanding of data transfe
In a groundbreaking study published in Nature Communications, an international team from Wits University and ICFO- The Institute of Photonic Sciences has unveiled a novel technique for transporting patterns of light, akin to image teleportation, across a network without the physical transmission of the image itself. This research not only challenges our conventional understanding of data transfe Satellite Communications Innovator Lynk Global to Go Public via Slam Corp. Merger
Tuesday, 19 December 2023 03:47 Lynk Global, Inc., a leader in satellite-to-phone communications, and Slam Corp. (NASDAQ: SLAM), a special purpose acquisition company, have embarked on a significant step towards merging. The two companies have signed a non-binding letter of intent (LOI) for a potential business combination. This move, once finalized, is set to list Lynk Global, Inc. as a publicly-traded entity under the ticker
Lynk Global, Inc., a leader in satellite-to-phone communications, and Slam Corp. (NASDAQ: SLAM), a special purpose acquisition company, have embarked on a significant step towards merging. The two companies have signed a non-binding letter of intent (LOI) for a potential business combination. This move, once finalized, is set to list Lynk Global, Inc. as a publicly-traded entity under the ticker Blue Origin scrubs return of New Shepard rocket flight due to technical issue
Tuesday, 19 December 2023 03:47 Blue Origin has scrubbed its first flight since last year's uncrewed booster mishap. Monday's launch in West Texas was called off earlier in the day, first for cold weather and then due to an unspecified "ground system issue."
"We're scrubbing #NS24 today due to a ground system issue the team is troubleshooting. We'll provide a new launch target for this week soon," Blue Origin revealed
Blue Origin has scrubbed its first flight since last year's uncrewed booster mishap. Monday's launch in West Texas was called off earlier in the day, first for cold weather and then due to an unspecified "ground system issue."
"We're scrubbing #NS24 today due to a ground system issue the team is troubleshooting. We'll provide a new launch target for this week soon," Blue Origin revealed Research unveils atmospheric dynamics of runaway greenhouse effect
Tuesday, 19 December 2023 03:47 A recent study by a team of astronomers from the University of Geneva (UNIGE), in collaboration with CNRS laboratories in Paris and Bordeaux, has successfully simulated the entire runaway greenhouse process, marking a significant advancement in understanding planetary climates. This process, which can dramatically transform a planet's climate from conducive to life to extremely hostile, has been
A recent study by a team of astronomers from the University of Geneva (UNIGE), in collaboration with CNRS laboratories in Paris and Bordeaux, has successfully simulated the entire runaway greenhouse process, marking a significant advancement in understanding planetary climates. This process, which can dramatically transform a planet's climate from conducive to life to extremely hostile, has been NASA's GUSTO Prepares to Map Space Between the Stars
Tuesday, 19 December 2023 03:47 On a vast ice sheet in Antarctica, scientists and engineers are preparing a NASA experiment called GUSTO to explore the universe on a balloon. GUSTO will launch from the Ross Ice Shelf, near the U.S. National Science Foundation's McMurdo Station research base, no earlier than Dec. 21.
GUSTO, which stands for Galactic/Extragalactic ULDB Spectroscopic Terahertz Observatory, will peer into th
On a vast ice sheet in Antarctica, scientists and engineers are preparing a NASA experiment called GUSTO to explore the universe on a balloon. GUSTO will launch from the Ross Ice Shelf, near the U.S. National Science Foundation's McMurdo Station research base, no earlier than Dec. 21.
GUSTO, which stands for Galactic/Extragalactic ULDB Spectroscopic Terahertz Observatory, will peer into th The feline frontier: NASA sends cat video from deep space
Tuesday, 19 December 2023 03:47 NASA on Monday announced it had used a state-of-the-art laser communication system on a spaceship 19 million miles (31 million kilometers) away from Earth - to send a high-definition cat video.
The 15-second meow-vie featuring an orange tabby named Taters is the first to be streamed from deep space, and demonstrates it's possible to transmit the higher-data-rate communications needed to sup
NASA on Monday announced it had used a state-of-the-art laser communication system on a spaceship 19 million miles (31 million kilometers) away from Earth - to send a high-definition cat video.
The 15-second meow-vie featuring an orange tabby named Taters is the first to be streamed from deep space, and demonstrates it's possible to transmit the higher-data-rate communications needed to sup Lynk Global plans to go public to fund direct-to-smartphone satellites
Monday, 18 December 2023 20:53

Photonic crystals could be exactly what Breakthrough Starshot is looking for
Monday, 18 December 2023 19:33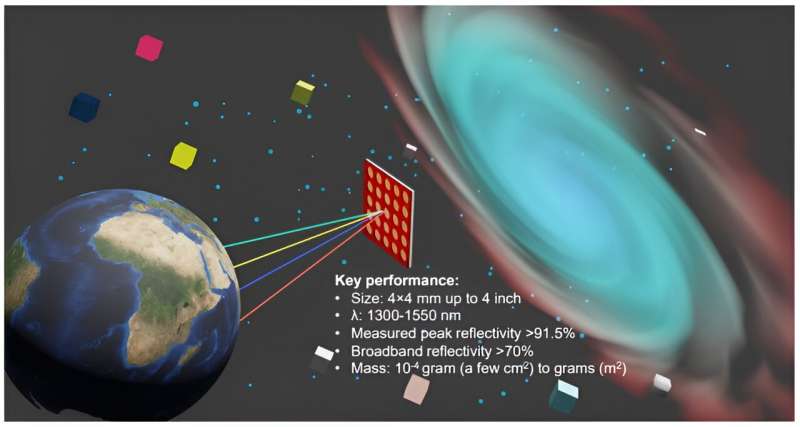
Light sail technology is a fascinating concept and a step change in rocket propulsion. It may not be big and impressive like the Saturn V, the Space Shuttle or the new Starship rocket but when it comes to traveling among the stars, light sails could just be the answer.
NASA's BurstCube passes milestones on journey to launch
Monday, 18 December 2023 19:31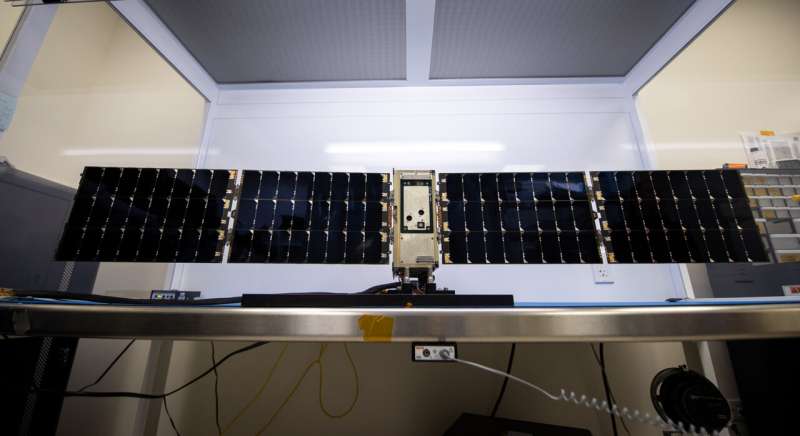
Scientists and engineers at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, have completed testing for BurstCube, a shoebox-sized spacecraft designed to study the universe's most powerful explosions. Members of the team have also delivered the satellite to their partner Nanoracks (part of Voyager Space) in Houston, Texas, where it will be packed for launch.
Report: Hypersonic weapons challenge Pentagon tracking capabilities
Monday, 18 December 2023 18:00

Jeff Bezos' Blue Origin pushes back return to space
Monday, 18 December 2023 15:12
Blue Origin on Monday postponed its long-awaited return to space, citing technical reasons and promising to try again later this week.
Jeff Bezos' space company has not launched a rocket since an uncrewed September 2022 crash placed its program on hold while it carried out fixes and awaited regulatory approval.
The company finally announced a December 18 launch from its base near Van Horn, Texas. But on the day itself it first pushed back the takeoff window because of cold weather, then declared it was off.
"We're scrubbing #NS24 today due to a ground system issue the team is troubleshooting. We'll provide a new launch target for this week soon," Blue posted on X, formerly Twitter.
Though the rocket will carry a payload of science experiments, not people, mission NS-24 must succeed before Blue Origin can return to taking wealthy thrill-seekers to the final frontier.
On September 12, 2022, a Blue Origin rocket became engulfed in flames shortly after launch.




