
Copernical Team
Tuesday, 24 September 2024 07:53
LUNA infographics
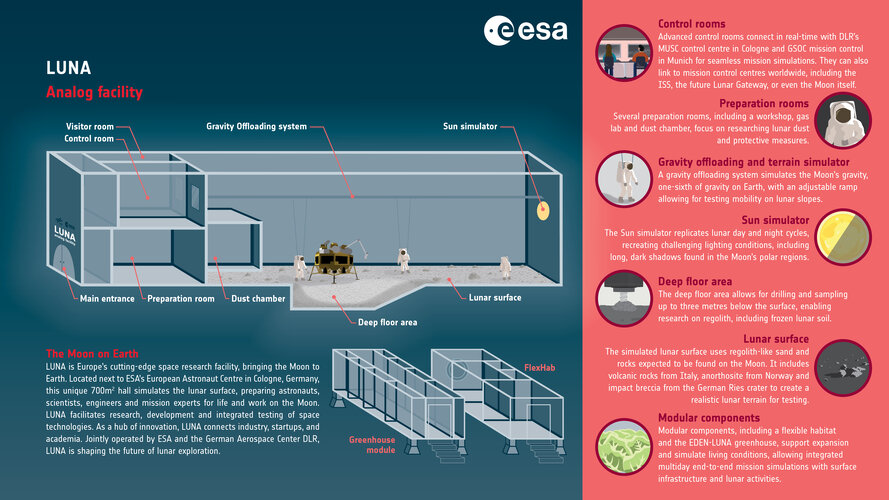 Image:
LUNA infographics
Image:
LUNA infographics
Published in
News
Tagged under
Tuesday, 24 September 2024 14:00
New study suggests Earth's mantle is more chemically uniform than previously thought
Los Angeles CA (SPX) Sep 20, 2024
 Lavas from volcanic hotspots around the world, such as Hawaii, Samoa, and Iceland, likely come from a chemically uniform reservoir in Earth's mantle, according to new research published in 'Nature Geoscience'. The study challenges the long-standing belief that the mantle contains chemically distinct reservoirs.
The research suggests that Earth's mantle is more homogeneous than scientists h
Lavas from volcanic hotspots around the world, such as Hawaii, Samoa, and Iceland, likely come from a chemically uniform reservoir in Earth's mantle, according to new research published in 'Nature Geoscience'. The study challenges the long-standing belief that the mantle contains chemically distinct reservoirs.
The research suggests that Earth's mantle is more homogeneous than scientists h
 Lavas from volcanic hotspots around the world, such as Hawaii, Samoa, and Iceland, likely come from a chemically uniform reservoir in Earth's mantle, according to new research published in 'Nature Geoscience'. The study challenges the long-standing belief that the mantle contains chemically distinct reservoirs.
The research suggests that Earth's mantle is more homogeneous than scientists h
Lavas from volcanic hotspots around the world, such as Hawaii, Samoa, and Iceland, likely come from a chemically uniform reservoir in Earth's mantle, according to new research published in 'Nature Geoscience'. The study challenges the long-standing belief that the mantle contains chemically distinct reservoirs.
The research suggests that Earth's mantle is more homogeneous than scientists h
Published in
News
Tagged under
Tuesday, 24 September 2024 14:00
Bridging the heavens and Earth
Boston MA (SPX) Sep 19, 2024
 When Jared Bryan talks about his seismology research, it's with a natural finesse. He's a fifth-year PhD student working with MIT Assistant Professor William Frank on seismology research, drawn in by the lab's combination of GPS observations, satellites, and seismic station data to understand the underlying physics of earthquakes. He has no trouble talking about seismic velocity in fault zones o
When Jared Bryan talks about his seismology research, it's with a natural finesse. He's a fifth-year PhD student working with MIT Assistant Professor William Frank on seismology research, drawn in by the lab's combination of GPS observations, satellites, and seismic station data to understand the underlying physics of earthquakes. He has no trouble talking about seismic velocity in fault zones o
 When Jared Bryan talks about his seismology research, it's with a natural finesse. He's a fifth-year PhD student working with MIT Assistant Professor William Frank on seismology research, drawn in by the lab's combination of GPS observations, satellites, and seismic station data to understand the underlying physics of earthquakes. He has no trouble talking about seismic velocity in fault zones o
When Jared Bryan talks about his seismology research, it's with a natural finesse. He's a fifth-year PhD student working with MIT Assistant Professor William Frank on seismology research, drawn in by the lab's combination of GPS observations, satellites, and seismic station data to understand the underlying physics of earthquakes. He has no trouble talking about seismic velocity in fault zones o
Published in
News
Tagged under
Tuesday, 24 September 2024 14:00
BlackSky secures HEO contract for Space Domain Awareness and Non-Earth Imaging
Los Angeles CA (SPX) Sep 20, 2024
 BlackSky Technology Inc. (NYSE: BKSY) has been awarded a seven-figure contract by HEO to advance its automated low-latency capabilities for non-Earth imaging (NEI) services, catering to defense, intelligence, and commercial sectors. The agreement will integrate BlackSky's satellite constellation into HEO's NEI sensor network. After successfully completing an initial proof of concept, the partner
BlackSky Technology Inc. (NYSE: BKSY) has been awarded a seven-figure contract by HEO to advance its automated low-latency capabilities for non-Earth imaging (NEI) services, catering to defense, intelligence, and commercial sectors. The agreement will integrate BlackSky's satellite constellation into HEO's NEI sensor network. After successfully completing an initial proof of concept, the partner
 BlackSky Technology Inc. (NYSE: BKSY) has been awarded a seven-figure contract by HEO to advance its automated low-latency capabilities for non-Earth imaging (NEI) services, catering to defense, intelligence, and commercial sectors. The agreement will integrate BlackSky's satellite constellation into HEO's NEI sensor network. After successfully completing an initial proof of concept, the partner
BlackSky Technology Inc. (NYSE: BKSY) has been awarded a seven-figure contract by HEO to advance its automated low-latency capabilities for non-Earth imaging (NEI) services, catering to defense, intelligence, and commercial sectors. The agreement will integrate BlackSky's satellite constellation into HEO's NEI sensor network. After successfully completing an initial proof of concept, the partner
Published in
News
Tagged under
Tuesday, 24 September 2024 14:00
Airbus Assigns GMV to Develop Navigation System for SIRTAP UAS
Madrid, Spain (SPX) Sep 19, 2024
 GMV has been chosen by Airbus to develop the navigation system for the SIRTAP (High Performance Remotely Operated System) tactical UAS. This contract covers both the onboard equipment and the ground augmentation station, aimed at enhancing navigation accuracy during crucial phases like takeoff and landing.
The SIRTAP unmanned aerial system is engineered for advanced intelligence, surveilla
GMV has been chosen by Airbus to develop the navigation system for the SIRTAP (High Performance Remotely Operated System) tactical UAS. This contract covers both the onboard equipment and the ground augmentation station, aimed at enhancing navigation accuracy during crucial phases like takeoff and landing.
The SIRTAP unmanned aerial system is engineered for advanced intelligence, surveilla
 GMV has been chosen by Airbus to develop the navigation system for the SIRTAP (High Performance Remotely Operated System) tactical UAS. This contract covers both the onboard equipment and the ground augmentation station, aimed at enhancing navigation accuracy during crucial phases like takeoff and landing.
The SIRTAP unmanned aerial system is engineered for advanced intelligence, surveilla
GMV has been chosen by Airbus to develop the navigation system for the SIRTAP (High Performance Remotely Operated System) tactical UAS. This contract covers both the onboard equipment and the ground augmentation station, aimed at enhancing navigation accuracy during crucial phases like takeoff and landing.
The SIRTAP unmanned aerial system is engineered for advanced intelligence, surveilla
Published in
News
Tagged under
Tuesday, 24 September 2024 14:00
Magnifying deep space through the "Carousel Lens"
Berkeley CA (SPX) Sep 19, 2024
 In a rare and extraordinary discovery, researchers have identified a unique configuration of galaxies that form the most exquisitely aligned gravitational lens found to date. The Carousel Lens is a massive cluster-scale gravitational lens system that will enable researchers to delve deeper into the mysteries of the cosmos, including dark matter and dark energy.
"This is an amazingly lucky
In a rare and extraordinary discovery, researchers have identified a unique configuration of galaxies that form the most exquisitely aligned gravitational lens found to date. The Carousel Lens is a massive cluster-scale gravitational lens system that will enable researchers to delve deeper into the mysteries of the cosmos, including dark matter and dark energy.
"This is an amazingly lucky
 In a rare and extraordinary discovery, researchers have identified a unique configuration of galaxies that form the most exquisitely aligned gravitational lens found to date. The Carousel Lens is a massive cluster-scale gravitational lens system that will enable researchers to delve deeper into the mysteries of the cosmos, including dark matter and dark energy.
"This is an amazingly lucky
In a rare and extraordinary discovery, researchers have identified a unique configuration of galaxies that form the most exquisitely aligned gravitational lens found to date. The Carousel Lens is a massive cluster-scale gravitational lens system that will enable researchers to delve deeper into the mysteries of the cosmos, including dark matter and dark energy.
"This is an amazingly lucky
Published in
News
Tagged under
Tuesday, 24 September 2024 14:00
CT Engineering introduces LAB_METOC to enhance space mission safety
Paris, France (SPX) Sep 22, 2024
 CT Engineering, a leader in technological innovation and engineering services, has unveiled its LAB_METOC platform, an advanced solution designed to improve the management of weather-sensitive space missions. The platform is expected to significantly enhance both the safety and efficiency of launch campaigns, benefiting operations in civil and military environments alike.
Space missions, p
CT Engineering, a leader in technological innovation and engineering services, has unveiled its LAB_METOC platform, an advanced solution designed to improve the management of weather-sensitive space missions. The platform is expected to significantly enhance both the safety and efficiency of launch campaigns, benefiting operations in civil and military environments alike.
Space missions, p
 CT Engineering, a leader in technological innovation and engineering services, has unveiled its LAB_METOC platform, an advanced solution designed to improve the management of weather-sensitive space missions. The platform is expected to significantly enhance both the safety and efficiency of launch campaigns, benefiting operations in civil and military environments alike.
Space missions, p
CT Engineering, a leader in technological innovation and engineering services, has unveiled its LAB_METOC platform, an advanced solution designed to improve the management of weather-sensitive space missions. The platform is expected to significantly enhance both the safety and efficiency of launch campaigns, benefiting operations in civil and military environments alike.
Space missions, p
Published in
News
Tagged under
Tuesday, 24 September 2024 14:00
Astranis secures cxontract to add military Ka band to Omega satellites
Los Angeles CA (SPX) Sep 20, 2024
 The U.S. Space Force's Space Systems Command (SSC) and U.S. Space Command (USSPACECOM) have awarded Astranis a $13.2 million contract to enhance their Omega satellites with Military Ka frequency capabilities. This contract includes $3.3 million of funding from SSC and is part of a Strategic Funding Increase (STRATFI) initiative, supported by Space Systems Command, SpaceWERX, and other venture ca
The U.S. Space Force's Space Systems Command (SSC) and U.S. Space Command (USSPACECOM) have awarded Astranis a $13.2 million contract to enhance their Omega satellites with Military Ka frequency capabilities. This contract includes $3.3 million of funding from SSC and is part of a Strategic Funding Increase (STRATFI) initiative, supported by Space Systems Command, SpaceWERX, and other venture ca
 The U.S. Space Force's Space Systems Command (SSC) and U.S. Space Command (USSPACECOM) have awarded Astranis a $13.2 million contract to enhance their Omega satellites with Military Ka frequency capabilities. This contract includes $3.3 million of funding from SSC and is part of a Strategic Funding Increase (STRATFI) initiative, supported by Space Systems Command, SpaceWERX, and other venture ca
The U.S. Space Force's Space Systems Command (SSC) and U.S. Space Command (USSPACECOM) have awarded Astranis a $13.2 million contract to enhance their Omega satellites with Military Ka frequency capabilities. This contract includes $3.3 million of funding from SSC and is part of a Strategic Funding Increase (STRATFI) initiative, supported by Space Systems Command, SpaceWERX, and other venture ca
Published in
News
Tagged under
Tuesday, 24 September 2024 14:00
Holistic approach to understanding Earth System science
Sydney, Australia (SPX) Sep 20, 2024
 A new white paper by a multidisciplinary team of scientists from China presents an expansive definition of Earth system science. The paper outlines that Earth's system includes both internal and external geospheres, spanning from the planet's core to the Sun-Earth space system. This broad approach covers a variety of components, including the solid Earth (core, mantle, and crust), the surface sy
A new white paper by a multidisciplinary team of scientists from China presents an expansive definition of Earth system science. The paper outlines that Earth's system includes both internal and external geospheres, spanning from the planet's core to the Sun-Earth space system. This broad approach covers a variety of components, including the solid Earth (core, mantle, and crust), the surface sy
 A new white paper by a multidisciplinary team of scientists from China presents an expansive definition of Earth system science. The paper outlines that Earth's system includes both internal and external geospheres, spanning from the planet's core to the Sun-Earth space system. This broad approach covers a variety of components, including the solid Earth (core, mantle, and crust), the surface sy
A new white paper by a multidisciplinary team of scientists from China presents an expansive definition of Earth system science. The paper outlines that Earth's system includes both internal and external geospheres, spanning from the planet's core to the Sun-Earth space system. This broad approach covers a variety of components, including the solid Earth (core, mantle, and crust), the surface sy
Published in
News
Tagged under
Tuesday, 24 September 2024 14:00
Russian cosmonauts return to Earth after record ISS stay
Almaty, Kazakhstan (AFP) Sept 23, 2024
 Two Russian cosmonauts landed back on Earth on Monday after a record-breaking stay aboard the International Space Station (ISS).
Oleg Kononenko and Nikolai Chub spent 374 days in low-Earth orbit at the ISS, the longest time anybody has ever stayed on the station in a continuous stint.
During his stay, Kononenko, 60, also set a new record for the longest cumulative time any person has spe
Two Russian cosmonauts landed back on Earth on Monday after a record-breaking stay aboard the International Space Station (ISS).
Oleg Kononenko and Nikolai Chub spent 374 days in low-Earth orbit at the ISS, the longest time anybody has ever stayed on the station in a continuous stint.
During his stay, Kononenko, 60, also set a new record for the longest cumulative time any person has spe
 Two Russian cosmonauts landed back on Earth on Monday after a record-breaking stay aboard the International Space Station (ISS).
Oleg Kononenko and Nikolai Chub spent 374 days in low-Earth orbit at the ISS, the longest time anybody has ever stayed on the station in a continuous stint.
During his stay, Kononenko, 60, also set a new record for the longest cumulative time any person has spe
Two Russian cosmonauts landed back on Earth on Monday after a record-breaking stay aboard the International Space Station (ISS).
Oleg Kononenko and Nikolai Chub spent 374 days in low-Earth orbit at the ISS, the longest time anybody has ever stayed on the station in a continuous stint.
During his stay, Kononenko, 60, also set a new record for the longest cumulative time any person has spe
Published in
News
Tagged under

