Copernical Team
Ariel Ekblaw on building beautiful architecture in space
 Living in space today is a cramped and utilitarian endeavor. Astronuats who arrive on the International Space Station (ISS) are prepared for a stay in tight quarters, surrounded by exposed wiring, bulky electronics, and floor-to-ceiling beige paneling.
But what if in-orbit accomodations could be more spacious, livable, and even beautiful? That's a question driving TESSERAE, an ambitious sp
Living in space today is a cramped and utilitarian endeavor. Astronuats who arrive on the International Space Station (ISS) are prepared for a stay in tight quarters, surrounded by exposed wiring, bulky electronics, and floor-to-ceiling beige paneling.
But what if in-orbit accomodations could be more spacious, livable, and even beautiful? That's a question driving TESSERAE, an ambitious sp Powering the moon: Sandia researchers design microgrid for future lunar base
 Sandia National Laboratories is well-known for designing reliable and resilient microgrids for military bases and vital city services. Now, Sandia researchers are working with NASA to design one for the moon.
This is not the first time Sandia has partnered with NASA to power equipment on the moon. In fact, Sandia provided the technical direction for the radioisotope thermoelectric generato
Sandia National Laboratories is well-known for designing reliable and resilient microgrids for military bases and vital city services. Now, Sandia researchers are working with NASA to design one for the moon.
This is not the first time Sandia has partnered with NASA to power equipment on the moon. In fact, Sandia provided the technical direction for the radioisotope thermoelectric generato Relations on ISS not changed following Russia's Invasion of Ukraine
 Relations on the International Space Station (ISS) have not changed amid Russia's ongoing [war] in Ukraine, NASA astronaut Tom Marshburn said on Wednesday.
"As far as the international relations go, that has not changed at all. We've had 40-plus year relationship with our international partners and with the Russian colleagues as well," Marshburn said. "[O]ne of the greatest legacies of the
Relations on the International Space Station (ISS) have not changed amid Russia's ongoing [war] in Ukraine, NASA astronaut Tom Marshburn said on Wednesday.
"As far as the international relations go, that has not changed at all. We've had 40-plus year relationship with our international partners and with the Russian colleagues as well," Marshburn said. "[O]ne of the greatest legacies of the USSF Space Test Enterprise Vision integrates test across capability lifecycles
 The Space Force has released its Space Test Enterprise Vision to communicate the service's intent and provide the amplifying guidance needed to execute the Space Force's test and evaluation mission.
"The test vision and the associated test culture it portends are critical elements of the Guardian Ideal and our core values," said Gen. David D. Thompson, Vice Chief of Space Operations. "Whil
The Space Force has released its Space Test Enterprise Vision to communicate the service's intent and provide the amplifying guidance needed to execute the Space Force's test and evaluation mission.
"The test vision and the associated test culture it portends are critical elements of the Guardian Ideal and our core values," said Gen. David D. Thompson, Vice Chief of Space Operations. "Whil Astronomers reveal first image of black hole at Milky Way's centre
 An international team of astronomers on Thursday unveiled the first image of a supermassive black hole at the centre of our own Milky Way galaxy - a cosmic body known as Sagittarius A*.
The image - produced by a global team of scientists known as the Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) Collaboration - is the first, direct visual confirmation of the presence of this invisible object, and comes th
An international team of astronomers on Thursday unveiled the first image of a supermassive black hole at the centre of our own Milky Way galaxy - a cosmic body known as Sagittarius A*.
The image - produced by a global team of scientists known as the Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) Collaboration - is the first, direct visual confirmation of the presence of this invisible object, and comes th Powering the moon: Designing a microgrid for future lunar base
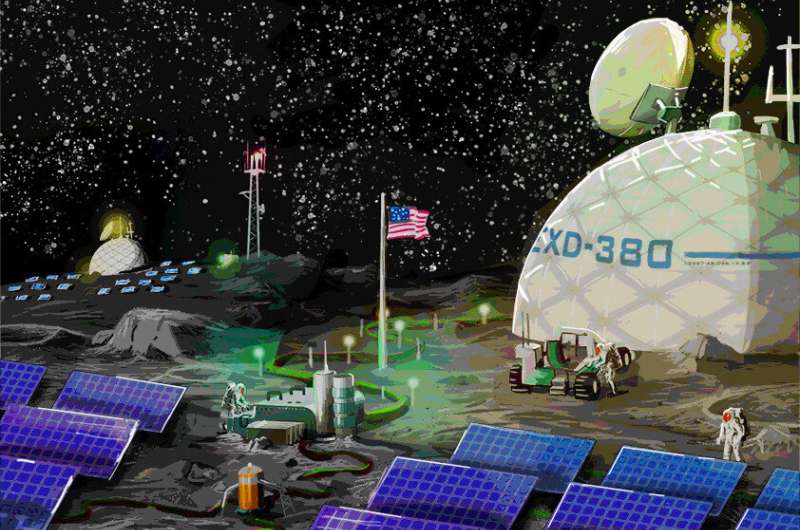

Sandia National Laboratories is well-known for designing reliable and resilient microgrids for military bases and vital city services. Now, Sandia researchers are working with NASA to design one for the moon.
This is not the first time Sandia has partnered with NASA to power equipment on the moon. In fact, Sandia provided the technical direction for the radioisotope thermoelectric generators that powered the lunar experiments placed by many of the Apollo missions.
NASA's plan for its concept Artemis lunar base is that it will serve as a technology proving ground for the eventual human exploration of Mars, said Jack Flicker, a Sandia electrical engineer.
Smarter satellites: ESA Discovery accelerates AI in space

Could we capitalise on the Earth-based digital revolution to make our satellites smarter?
ESA Discovery is funding 12 projects that will explore the potential of applying the latest developments in artificial intelligence (AI) and advanced computing paradigms to make satellites more reactive, agile and autonomous. This could generate new practical applications that support life on Earth and our exploration of other planets.
UK company reveals micro-launcher rocket
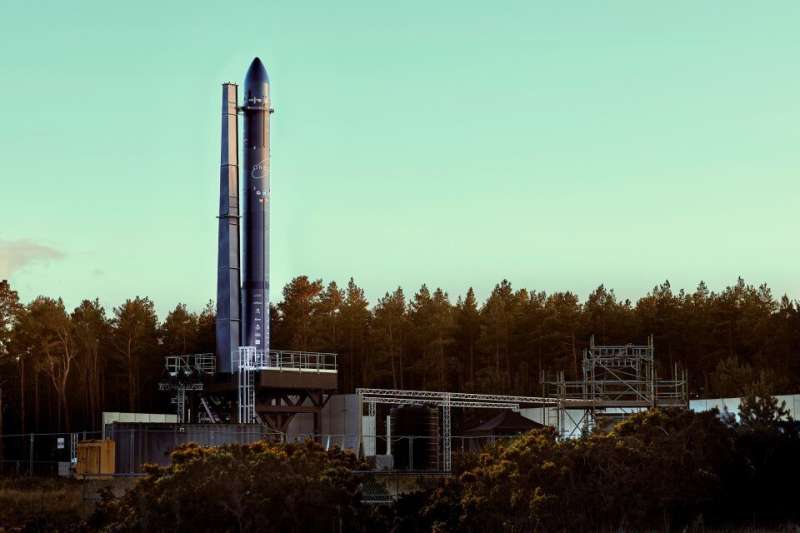

Orbex's Prime rocket reaching technical readiness represents a significant achievement that brings together key elements of the ground infrastructure and prototype launch vehicle for the first time and is a major step forward for the company and for the U.K. launch industry.
The U.K. Space Agency supported the development of Orbex's Prime rocket with £5.5 million of funding, as part of the government's plans to enable small satellite launch from U.K. spaceports.
With the first integration of a full scale Orbex prototype launch vehicle on a launch pad now complete, the company will enter a period of integrated testing, allowing dress rehearsals of rocket launches and the development and optimization of launch procedures.
Orbex recently revealed their first test launch platform at a new test facility in Kinloss, a few miles from the company's headquarters at Forres in Moray, Scotland.
Science Minister George Freeman said: "This is a hugely exciting time for the U.K. space and satellite sector as we count down to the first satellite launches from U.K. spaceports later this summer. Orbex Prime is a remarkable feat of engineering from a British rocket company, pioneering more sustainable and innovative fuels that cut carbon emissions.
What's the best way to build landing pads on the moon?
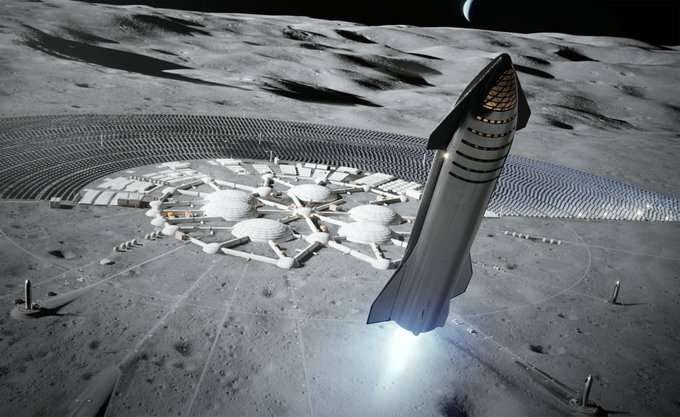

In the near future, NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA), China, and Roscosmos all mount crewed missions to the moon. This will constitute the first time astronauts have walked on the lunar surface since the Apollo era. But unlike the "race to the moon," the goal of these programs is not to get there first and leave only a few experiments and landers behind (i.e., "footprints and flags" missions), but to establish a sustained human presence on the lunar surface. This means creating habitats on the surface and in orbit that can be used by rotating crews.
While NASA and other space agencies intend to leverage local resources as much as possible—a process known as in-situ resource utilization (ISRU)—creating lunar bases will still require lots of materials and machinery to be shipped from Earth. In a recent study, Philip Metzger and Greg Autry reviewed the cost and energy consumption of building landing pads on the lunar surface.
Wealthy nations are carving up space and its riches, and leaving other countries behind

Satellites help run the internet and television and are central to the Global Positioning System. They enable modern weather forecasting, help scientists track environmental degradation and play a huge role in modern military technology.
Nations that don't have their own satellites providing these services rely on other countries. For those that want to develop their own satellite infrastructure, options are running out as space fills up.
I am a research fellow at Arizona State University, studying the wider benefits of space and ways to make it more accessible to developing countries.