Copernical Team
Sidus Space awarded additional SLS contracts
 Sidus Space (NASDAQ: SIDU) has received additional hardware manufacturing subcontracts to support NASA's Artemis Program and Space Launch System ("SLS") Manned Vehicle. Under the terms of the subcontract between Sidus Space and Craig Technologies, Sidus will be responsible for the fabrication of the Umbilical Quick Disconnects on the Universal Stage Adapter for the SLS. Dynetics (NYSE: LDOS), is
Sidus Space (NASDAQ: SIDU) has received additional hardware manufacturing subcontracts to support NASA's Artemis Program and Space Launch System ("SLS") Manned Vehicle. Under the terms of the subcontract between Sidus Space and Craig Technologies, Sidus will be responsible for the fabrication of the Umbilical Quick Disconnects on the Universal Stage Adapter for the SLS. Dynetics (NYSE: LDOS), is Dream Chaser comes to life
 In an important milestone for space travel technology, Sierra Space announced the successful power-up of its revolutionary Dream Chaser spaceplane. The test conducted by the company signifies the activation of the spacecraft's integrated systems and demonstrates the culmination of several years of meticulous engineering, design, and testing efforts.
The Dream Chaser, with its unique liftin
In an important milestone for space travel technology, Sierra Space announced the successful power-up of its revolutionary Dream Chaser spaceplane. The test conducted by the company signifies the activation of the spacecraft's integrated systems and demonstrates the culmination of several years of meticulous engineering, design, and testing efforts.
The Dream Chaser, with its unique liftin Weather delay moves SpaceX resupply mission to same day as Starlink launch
 Weather in Florida has delayed the launch of the SpaceX Dragon cargo mission, which is now slated to lift off Sunday, the same day the company also plans to send a new batch of Starlink satellites into orbit.
A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket is now scheduled to launch at 12:12 p.m. Sunday to send an automated Dragon cargo capsule to the International Space Station.
However, the company s
Weather in Florida has delayed the launch of the SpaceX Dragon cargo mission, which is now slated to lift off Sunday, the same day the company also plans to send a new batch of Starlink satellites into orbit.
A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket is now scheduled to launch at 12:12 p.m. Sunday to send an automated Dragon cargo capsule to the International Space Station.
However, the company s First-of-its-kind Mars livestream by ESA spacecraft interrupted at times by rain on Earth
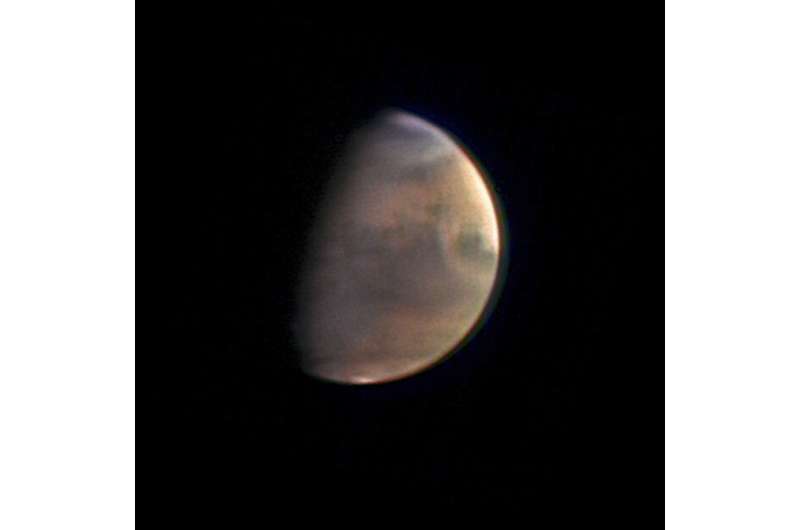

A European spacecraft around Mars sent its first livestream from the red planet to Earth on Friday to mark the 20th anniversary of its launch, but rain in Spain interfered at times.
Study reveals understanding of a basic physical property of charged particles in microgravity
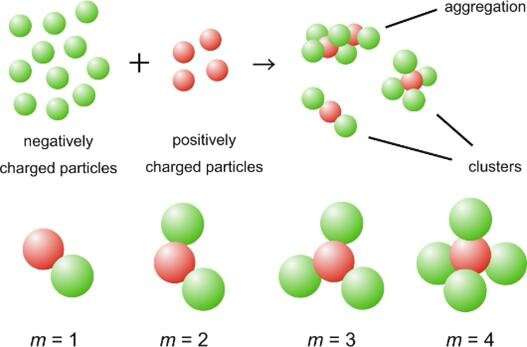
A study conducted by group of scientists from Nagoya City University (NCU), Japan Space Forum (JSF), Advance Engineering Services (AES), Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) and ANSTO has revealed a clustering of charged particles in the microgravity environment of International Space Station (ISS), with implications for the development of photonic materials, improved drugs, and a range of new and innovative materials that depend on the mixing of two or more charged particles.
The experimental study, which was published in npj Microgravity, and conducted on the ISS, determined how sub-micron sized charged colloidal particles interact in the presence and absence of Earth's gravity.
European Service Module-2 on the move
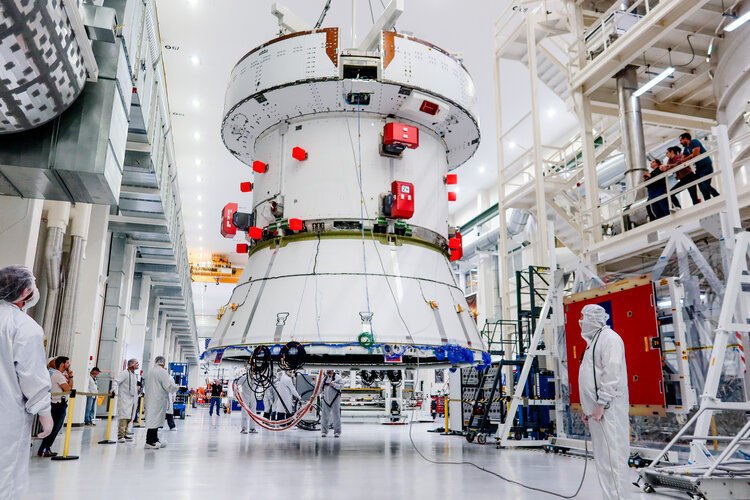 Image:
European Service Module-2 on the move
Image:
European Service Module-2 on the move Metal fuel for carbon-free energy on Earth and the Moon
 Everything burns. Given the right environment, all matter can burn by adding oxygen, but finding the right mix and generating enough heat makes some materials combust more easily than others. Researchers interested in knowing more about a type of fire called discrete burning used ESA's microgravity experiment facilities to investigate.
In a series of parabolic flights and on sounding rocke
Everything burns. Given the right environment, all matter can burn by adding oxygen, but finding the right mix and generating enough heat makes some materials combust more easily than others. Researchers interested in knowing more about a type of fire called discrete burning used ESA's microgravity experiment facilities to investigate.
In a series of parabolic flights and on sounding rocke US Air Force announces preferred locations for STARCOM HQ, three Deltas
 The Department of the Air Force selected Patrick Space Force Base, Florida, as the preferred location to host the Space Training and Readiness Command Headquarters, along with Space Delta 10. Kirtland Air Force Base, New Mexico, is the preferred location for Space Delta 11, and Schriever Space Force Base, Colorado, is the preferred location for Space Delta 12.
STARCOM, one of three U.S. Spac
The Department of the Air Force selected Patrick Space Force Base, Florida, as the preferred location to host the Space Training and Readiness Command Headquarters, along with Space Delta 10. Kirtland Air Force Base, New Mexico, is the preferred location for Space Delta 11, and Schriever Space Force Base, Colorado, is the preferred location for Space Delta 12.
STARCOM, one of three U.S. Spac Colorado Springs to host DEL 15, two additional squadrons
 The U.S. Space Force's Space Delta 15, activated in March 2023, is expected to be permanently based at Schriever Space Force Base, Colorado, along with the new 75th Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance Squadron. Additionally, the service expects the 74th ISR Squadron, activated in November 2022, to be based at Peterson Space Force Base, Colorado.
DEL 15, a command-and-control org
The U.S. Space Force's Space Delta 15, activated in March 2023, is expected to be permanently based at Schriever Space Force Base, Colorado, along with the new 75th Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance Squadron. Additionally, the service expects the 74th ISR Squadron, activated in November 2022, to be based at Peterson Space Force Base, Colorado.
DEL 15, a command-and-control org NASA grant funds aeroacoustic research to develop quieter vertical lift air vehicles
 Drone delivery is rapidly taking off in major cities, with rotor-powered rideshares not far behind. The convenience promised by electric vertical take-off and landing vehicles generates a substantial buzz - not just from excitement but from all the noise generated by rotors filling the sky.
To address key challenges facing the future of air transport, NASA has awarded $5.7 million to a mul
Drone delivery is rapidly taking off in major cities, with rotor-powered rideshares not far behind. The convenience promised by electric vertical take-off and landing vehicles generates a substantial buzz - not just from excitement but from all the noise generated by rotors filling the sky.
To address key challenges facing the future of air transport, NASA has awarded $5.7 million to a mul