Copernical Team
Orbiting astronaut oversees robot team on Earth
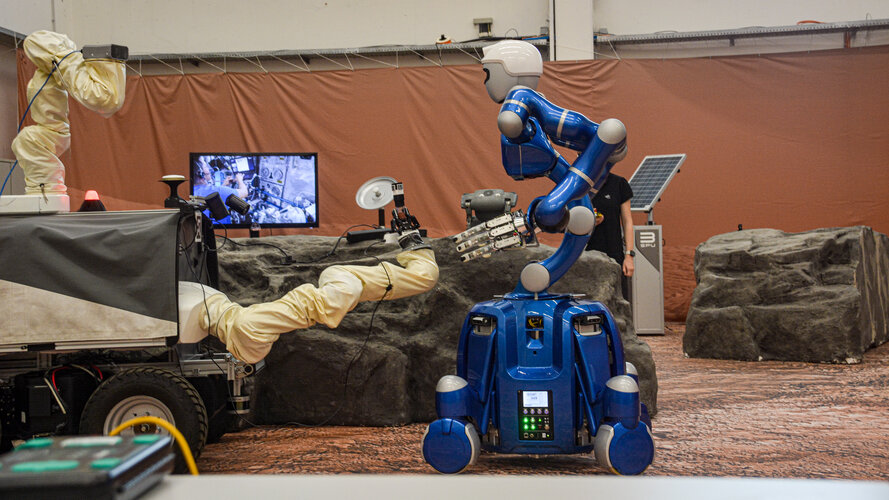

Astronaut Frank Rubio aboard the International Space Station collaborated with a small team of robots on Earth to accomplish a complex task – a first test of a new approach to combine human and robotic capabilities for our return to the Moon and beyond.
Teams selected to teach AI Agents to interact with people and learn
 As part of DARPA's Environment-driven Conceptual Learning (ECOLE) program, several university teams and industry performers will attempt to create artificial intelligence (AI) agents capable of continually learning from linguistic and visual input. Resulting agents would be able to collaborate with humans to help them produce analyses of image, video, and multimedia documents during time-sensiti
As part of DARPA's Environment-driven Conceptual Learning (ECOLE) program, several university teams and industry performers will attempt to create artificial intelligence (AI) agents capable of continually learning from linguistic and visual input. Resulting agents would be able to collaborate with humans to help them produce analyses of image, video, and multimedia documents during time-sensiti Consortium explores energy-efficient electronics and photonics
World's first methane-fueled rocket makes history, courtesy of LandSpace and GCL
 LandSpace, in partnership with GCL System Integration Technology Co., Ltd. (GCL), has successfully launched the world's first methane-powered rocket, Zhuque-2 (ZQ-2 Y2), into orbit. The launch took place at 9 a.m. (0100 GMT) from the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center in northwest China.
GCL, a global pioneer in renewable energy services, was instrumental in the development of Zhuque-2. This
LandSpace, in partnership with GCL System Integration Technology Co., Ltd. (GCL), has successfully launched the world's first methane-powered rocket, Zhuque-2 (ZQ-2 Y2), into orbit. The launch took place at 9 a.m. (0100 GMT) from the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center in northwest China.
GCL, a global pioneer in renewable energy services, was instrumental in the development of Zhuque-2. This Rocket Lab set to boost Capella's satellite constellation with upcoming launch
 Rocket Lab USA, Inc. (Nasdaq: RKLB) has scheduled its next Electron launch during a window that opens 28 July 2023 NZST/UTC.
The mission, named 'We Love the Nightlife,' is slated to commence during a launch window that opens on July 28, 2023 NZST/UTC. The launch site will be Rocket Lab Launch Complex 1, positioned on New Zealand's picturesque Mahia Peninsula.
American space tech firm
Rocket Lab USA, Inc. (Nasdaq: RKLB) has scheduled its next Electron launch during a window that opens 28 July 2023 NZST/UTC.
The mission, named 'We Love the Nightlife,' is slated to commence during a launch window that opens on July 28, 2023 NZST/UTC. The launch site will be Rocket Lab Launch Complex 1, positioned on New Zealand's picturesque Mahia Peninsula.
American space tech firm Kuaizhou 1A launches satellites into orbit
 China's state-owned China Aerospace Science and Industry Corp (CASIC) successfully launched a Kuaizhou 1A carrier rocket from the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center, located in China's northwestern desert, on Thursday morning. The mission's primary objective was to place four new weather satellites into orbit, enhancing the country's atmospheric data collection capabilities.
The Kuaizhou 1A,
China's state-owned China Aerospace Science and Industry Corp (CASIC) successfully launched a Kuaizhou 1A carrier rocket from the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center, located in China's northwestern desert, on Thursday morning. The mission's primary objective was to place four new weather satellites into orbit, enhancing the country's atmospheric data collection capabilities.
The Kuaizhou 1A, Groundbreaking method to speed up aerosol retrieval data from Chinese optical satellite
 A groundbreaking method for rapidly obtaining detailed observations of atmospheric aerosols via a new Chinese optical satellite has been proposed by a team of scientists. Aerosols, atmospheric particles that have a significant impact on our planet's climate system, influence solar and terrestrial radiation, and modify cloud properties.
While the launch of new satellite sensors often comes
A groundbreaking method for rapidly obtaining detailed observations of atmospheric aerosols via a new Chinese optical satellite has been proposed by a team of scientists. Aerosols, atmospheric particles that have a significant impact on our planet's climate system, influence solar and terrestrial radiation, and modify cloud properties.
While the launch of new satellite sensors often comes Thales announces Quantum-Ready Cybersecurity measures for Galileo
 Thales, the French multinational company, has affirmed its central role in providing cybersecurity solutions for Galileo, the global navigation satellite system (GNSS) that provides geolocation services. Thales, leading a consortium which includes Italian firm Leonardo, is tasked with expanding the G2G IOV SECMON project's security monitoring scope, incorporating new assets into the G2G system.
Thales, the French multinational company, has affirmed its central role in providing cybersecurity solutions for Galileo, the global navigation satellite system (GNSS) that provides geolocation services. Thales, leading a consortium which includes Italian firm Leonardo, is tasked with expanding the G2G IOV SECMON project's security monitoring scope, incorporating new assets into the G2G system. A faster way to teach a robot
 Imagine purchasing a robot to perform household tasks. This robot was built and trained in a factory on a certain set of tasks and has never seen the items in your home. When you ask it to pick up a mug from your kitchen table, it might not recognize your mug (perhaps because this mug is painted with an unusual image, say, of MIT's mascot, Tim the Beaver). So, the robot fails.
"Right now,
Imagine purchasing a robot to perform household tasks. This robot was built and trained in a factory on a certain set of tasks and has never seen the items in your home. When you ask it to pick up a mug from your kitchen table, it might not recognize your mug (perhaps because this mug is painted with an unusual image, say, of MIT's mascot, Tim the Beaver). So, the robot fails.
"Right now, How do microbes spread globally
 The study "Understanding atmospheric intercontinental dispersal of harmful microorganisms"* compiles the scope of the problem of the global dispersal of harmful microorganisms through the upper layers of the atmosphere. It confirms that the atmosphere -specifically the free troposphere- acts as a highway for many microbes and emphasizes the mechanisms that facilitate it.
The work combines
The study "Understanding atmospheric intercontinental dispersal of harmful microorganisms"* compiles the scope of the problem of the global dispersal of harmful microorganisms through the upper layers of the atmosphere. It confirms that the atmosphere -specifically the free troposphere- acts as a highway for many microbes and emphasizes the mechanisms that facilitate it.
The work combines