Copernical Team
A method for traction ability research of rover wheels on mixed planet terrain with movable stones
The Chang'e-6/7/8 exploration mission has been announced officially by China recently, and the international lunar and Mars research station plans will be carried out within the 2030s. It can be predicted that China's future lunar and Mars surface exploration activities will last longer, have a larger exploration range, and have a more complex terrain to traverse and explore, which will pose severe challenges to the working performance of the planet rover and its adaptability to the planet surface environment.
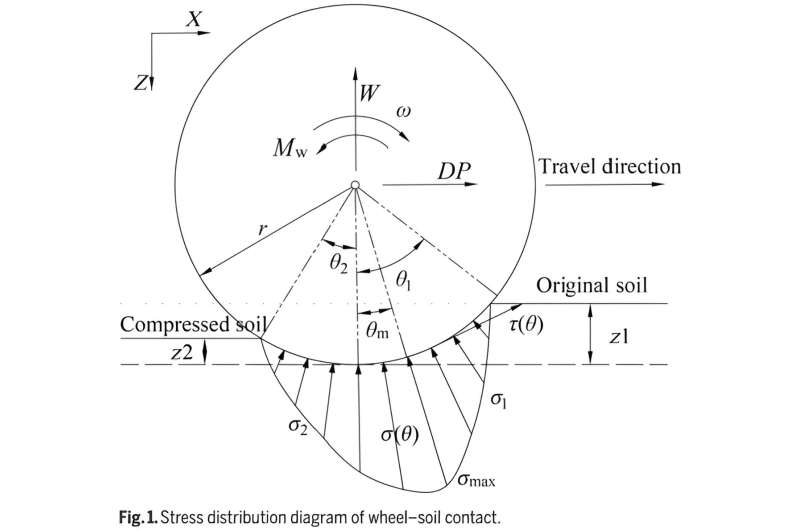
One of the key problems will be to study the relationship between the mechanical properties of planet soil and the traction performance of the planet rover's wheels. The mixed terrains of terramechanics research are mainly composed of static stones and loose soil.
Whereas, the movement behavior of stones is often ignored while analyzing the influence of the wheel's traction performance caused by mixed terrain.
The Astronaut Center of China 90-d head-down bed rest: Overview, countermeasures, and effects
When astronauts enter space, they are exposed to weightlessness. Physiological and psychological challenges are waiting ahead. They may have a puffy face and experience space motion sickness, cardiovascular deconditioning, muscle atrophy, and bone loss.
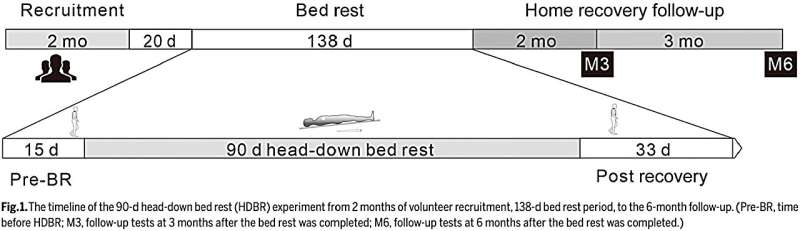
Moreover, long-term spaceflight has been shown to result in 83% of astronauts with post-flight orthostatic intolerance. For such problems, exercise countermeasures can be the primary approach to resolve these changes. Head-down bed rest (HDBR) simulates physiological effects in weightlessness and is widely used in countermeasure testing, and efficacy of exercise interventions has been widely studied in HDBR with different periods as well.
Usually, the long-term bed rest experiment is completed in stages, and a positive control of separated exercise countermeasures rarely tests at the same time in these experiments.
International Space Station tests show that a surface treatment can help prevent formation of biofilms in space
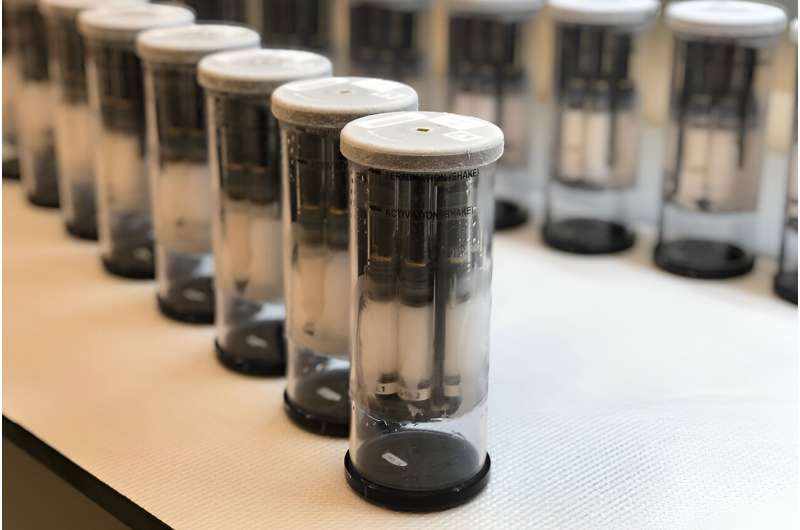

After exposure in space aboard the International Space Station, a new kind of surface treatment significantly reduced the growth of biofilms, scientists report. Biofilms are mats of microbial or fungal growth that can clog hoses or filters in water processing systems, or potentially cause illness in people.
Japan launches rocket carrying lunar lander and X-ray telescope to explore origins of universe
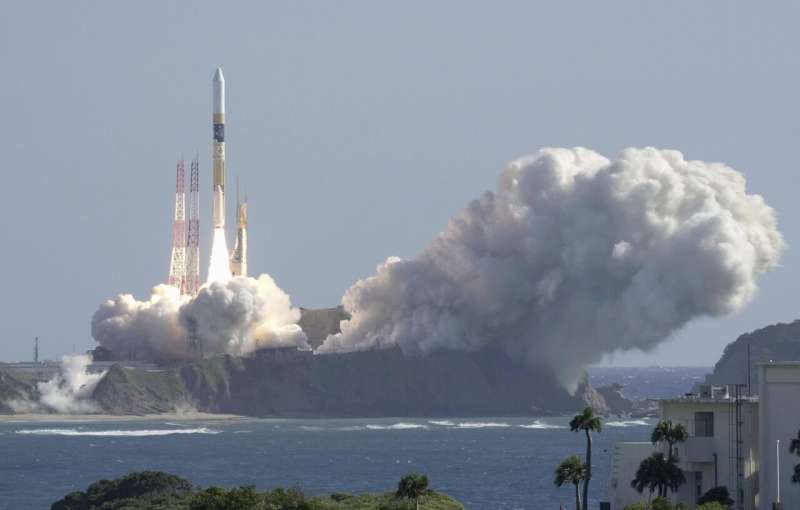

Japan launched a rocket Thursday carrying an X-ray telescope that will explore the origins of the universe as well as a small lunar lander.
The launch of the HII-A rocket from Tanegashima Space Center in southwestern Japan was shown on live video by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency, known as JAXA.
"We have a liftoff," the narrator at JAXA said as the rocket flew up in a burst of smoke then flew over the Pacific.
Thirteen minutes after the launch, the rocket put into orbit around Earth a satellite called the X-Ray Imaging and Spectroscopy Mission, or XRISM, which will measure the speed and makeup of what lies between galaxies.
Across the Northern Hemisphere, now's the time to catch a new comet before it vanishes for 400 years
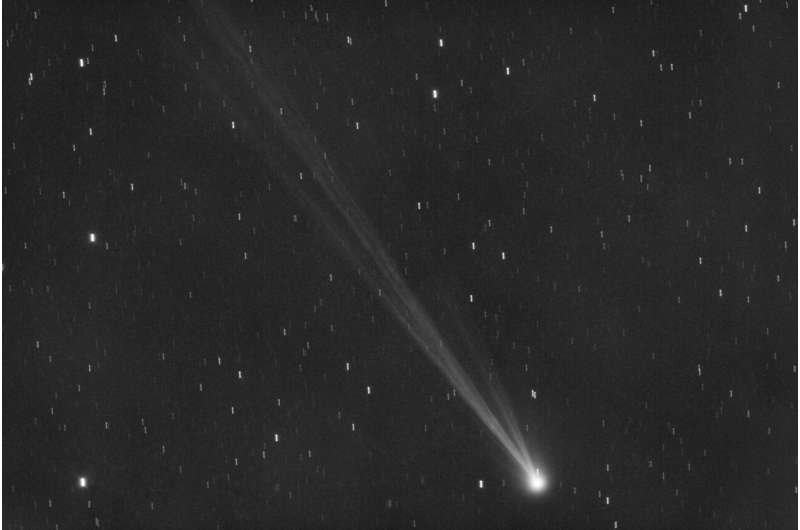

A newly discovered comet is swinging through our cosmic neighborhood for the first time in more than 400 years.
SpaceX awaits FAA approval for Starship launch
 Elon Musk said Tuesday that SpaceX is ready to launch a second test flight of its Starship and awaits Federal Aviation Administration approval nearly five months after the first test in Texas exploded over the Gulf of Mexico.
The updated Starship, the most powerful rocket ever built, was rolled out to the launching pad where it will wait for FAA approval before setting a new date for li
Elon Musk said Tuesday that SpaceX is ready to launch a second test flight of its Starship and awaits Federal Aviation Administration approval nearly five months after the first test in Texas exploded over the Gulf of Mexico.
The updated Starship, the most powerful rocket ever built, was rolled out to the launching pad where it will wait for FAA approval before setting a new date for li Japan launches 'Moon Sniper' mission
 Japan's "Moon Sniper" mission blasted off Thursday as the country's space programme looks to bounce back from a string of recent mishaps, weeks after India's historic lunar triumph.
Only the United States, Russia, China and as of last month India have successfully landed a probe on the Moon, with two failed Japanese missions - one public and one private.
Watched by 35,000 people online,
Japan's "Moon Sniper" mission blasted off Thursday as the country's space programme looks to bounce back from a string of recent mishaps, weeks after India's historic lunar triumph.
Only the United States, Russia, China and as of last month India have successfully landed a probe on the Moon, with two failed Japanese missions - one public and one private.
Watched by 35,000 people online, Japan launches telescope and moon lander following weather delays
 The Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency successfully launched a rocket Wednesday, with a high-powered X-ray telescope and moon lander on board, after the launch was scrubbed late last month due to high winds.
The H-2A rocket lifted off on time, at 7:42 p.m. EST, or 8:42 a.m. local time, from the Tanegashima Space Center in Japan, and deployed the space telescope on schedule.
"We ha
The Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency successfully launched a rocket Wednesday, with a high-powered X-ray telescope and moon lander on board, after the launch was scrubbed late last month due to high winds.
The H-2A rocket lifted off on time, at 7:42 p.m. EST, or 8:42 a.m. local time, from the Tanegashima Space Center in Japan, and deployed the space telescope on schedule.
"We ha Lightning in a camera – from above

ESA astronaut Andreas Mogensen will film thunderstorms and lightning shooting up towards space as part of the climate science of the Huginn mission.
Artificial star
 Image:
Artificial star
Image:
Artificial star