NASA completes mega-moon rocket stacking
Friday, 22 October 2021 17:25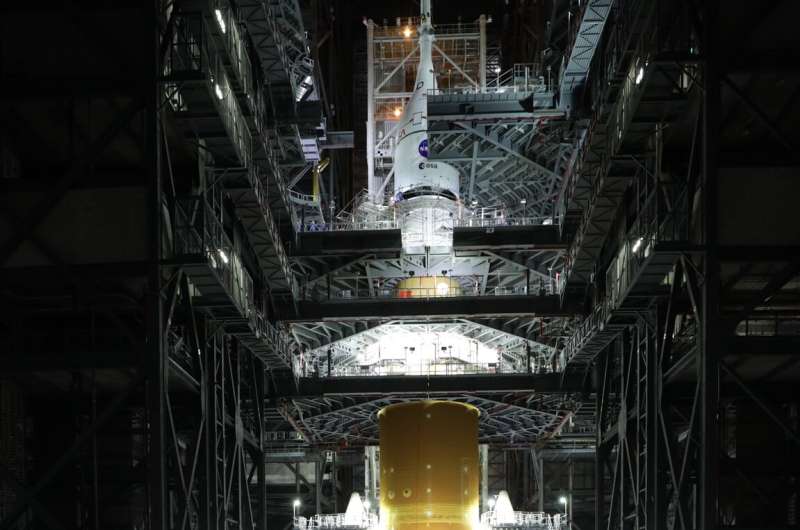
NASA has completed stacking of the agency's mega-Moon rocket and spacecraft that will launch the next generation of deep space operations, including Artemis missions on and around the Moon. Engineers and technicians successfully secured the Orion spacecraft atop the fully assembled Space Launch System (SLS) rocket at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida just before midnight Oct.
NASA Invites Media to Launch of IXPE Mission to Study X-rays in Space
Friday, 22 October 2021 16:59 Media accreditation is open for the upcoming launch of NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) mission, which will measure polarized X-rays from exotic cosmic objects, such as black holes and neutron stars, to better understand these types of phenomena and extreme environments.
Media accreditation is open for the upcoming launch of NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) mission, which will measure polarized X-rays from exotic cosmic objects, such as black holes and neutron stars, to better understand these types of phenomena and extreme environments. Artemis I stacked
Friday, 22 October 2021 14:30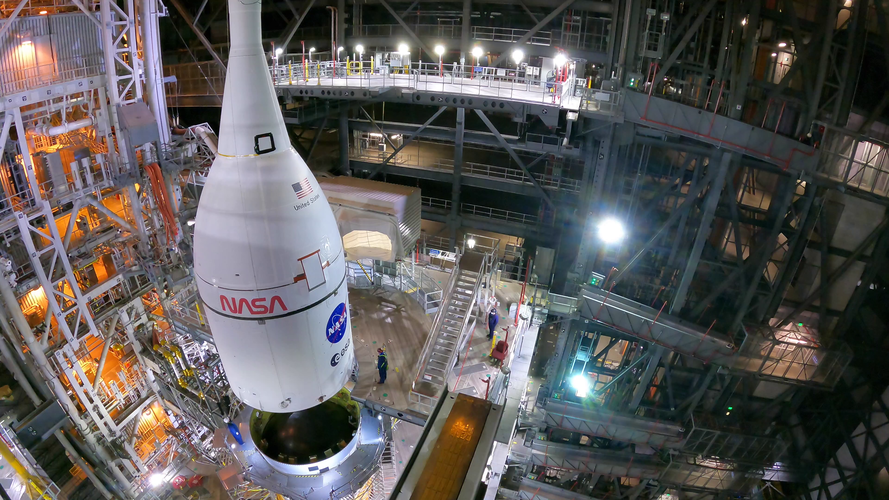 Video:
00:04:28
Video:
00:04:28
Time lapse of the stacking of the Orion spacecraft on top of the fully assembled Space Launch System (SLS) rocket at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on 21 October 2021, in preparation for the uncrewed Artemis I launch.
For Artemis I, the European Service Module will take the spacecraft more than 64 000 km beyond the Moon in a test flight to demonstrate its capabilities.
The European Service Module is ESA’s contribution to NASA’s Orion spacecraft that will send astronauts to the Moon and beyond. It provides electricity, water, oxygen and nitrogen as well as keeping the spacecraft at the right temperature
Male mice exposed to simulated deep space radiation experienced impaired spatial learning
Friday, 22 October 2021 14:00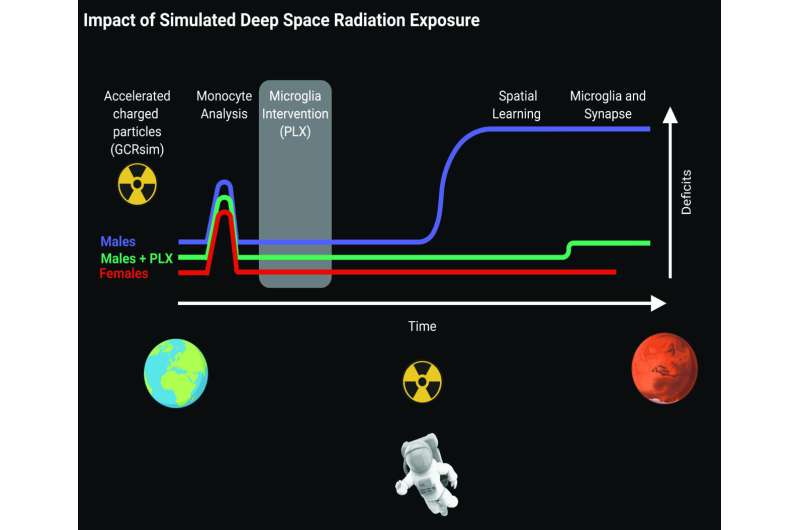
Seattle students virtually Zoom into space for a chat with astronaut Megan McArthur
Friday, 22 October 2021 13:48
The students gathered at the Museum of Flight in Seattle were ready to ask Megan McArthur questions, via video link, about life as an astronaut. She was about as far away as Walla Walla—but in outer space.
McArthur is a NASA astronaut aboard the International Space Station, moving above the Earth at more than 17,500 mph, orbiting every 90 minutes.
Just before the video connection was made for the Saturday event, former astronaut Dottie Metcalf-Lindenburger, an astronaut from 2004 to 2014, spoke about life aboard the space station and was asked, of course, everyone's favorite question: How do you go to the bathroom in space?
The answer: There are spacesuit hookups and funnels and toilets. Nothing floats free.
She was asked about the space station's size, and replied that it was a surprise to her how large it was. It's about the size of a soccer field, and the crew quarters—seven astronauts are currently at the station—are about the size of the interior of a Boeing 747 jumbo jet.
Then from space came a question: "Dottie, can you read me?"
Major step in UK contribution to space mission to study solar wind
Friday, 22 October 2021 13:48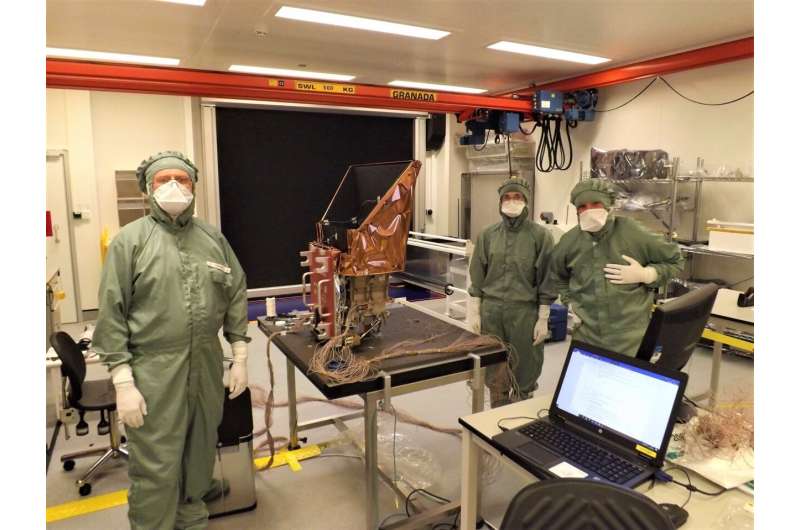
Space scientists from the University of Leicester have delivered a key component for a new mission to study the impact of the solar wind on Earth's magnetic field.
Engineers from the University's Space Research Centre have completed the structural and thermal model for the UK's latest X-ray telescope, the Soft X-ray Imager (SXI), destined for space aboard the SMILE (Solar wind Magnetosphere Ionosphere Link Explorer) probe when it launches at the end of 2024.
The model, which has now been delivered to Airbus in Spain for integration and testing within the prototype satellite system, is not the so-called flight model—but will help engineers understand the extreme requirements for the final design.
Week in images: 18 - 22 October 2021
Friday, 22 October 2021 12:39
Week in images: 18 - 22 October 2021
Discover our week through the lens
Proba-1 Celebrates 20th Birthday In Orbit
Friday, 22 October 2021 11:51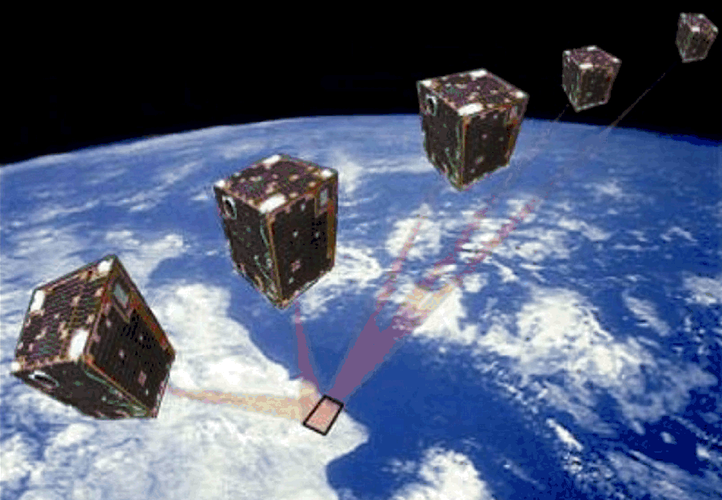
On this day, twenty years ago, ESA’s first small satellite, Proba-1 (Project for On Board Autonomy), was launched with just one goal – to prove technologies in space.
US conducts 'successful' test of hypersonic missile technology
Friday, 22 October 2021 10:48 The United States successfully tested hypersonic missile technology, a new weapons system which is already being deployed by China and Russia, the US Navy said Thursday.
The test, conducted Wednesday at a NASA facility in Wallops, Virginia, is a "vital step in the development of a Navy-designed common hypersonic missile," the navy said in a statement.
"This test demonstrated advanced hyp
The United States successfully tested hypersonic missile technology, a new weapons system which is already being deployed by China and Russia, the US Navy said Thursday.
The test, conducted Wednesday at a NASA facility in Wallops, Virginia, is a "vital step in the development of a Navy-designed common hypersonic missile," the navy said in a statement.
"This test demonstrated advanced hyp US and UK research labs collaborate on autonomy and artificial intelligence
Friday, 22 October 2021 10:48 The Air Force Research Laboratory, in partnership with UK's Defence Science and Technology Laboratory (Dstl), have demonstrated for the first time the ability for the U.S. and the UK to jointly develop, select, train, and deploy state-of-the-art machine learning algorithms in support of the Armed Forces of each of the two nations.
This research is designed to support adjacent, collaboratin
The Air Force Research Laboratory, in partnership with UK's Defence Science and Technology Laboratory (Dstl), have demonstrated for the first time the ability for the U.S. and the UK to jointly develop, select, train, and deploy state-of-the-art machine learning algorithms in support of the Armed Forces of each of the two nations.
This research is designed to support adjacent, collaboratin AMOS' compact hyperspectral instrument "ELOIS" to onboard a microsatellite soon
Friday, 22 October 2021 10:48 AMOS and the European Space Agency (ESA) have signed a contract to build and qualify a first flight model of an advanced compact hyperspectral imager designed by AMOS and called ELOIS.
Thanks to the financial support of the Belgian Science Policy Office (BELSPO), this co-funded project will deliver the payload to be integrated on an InnoSat platform by OHB Sweden AB for a launch in 2024. B
AMOS and the European Space Agency (ESA) have signed a contract to build and qualify a first flight model of an advanced compact hyperspectral imager designed by AMOS and called ELOIS.
Thanks to the financial support of the Belgian Science Policy Office (BELSPO), this co-funded project will deliver the payload to be integrated on an InnoSat platform by OHB Sweden AB for a launch in 2024. B DARPA moving SSITH safeguards closer to practical use
Friday, 22 October 2021 10:48 DARPA's System Security Integration Through Hardware and firmware (SSITH) program is exploring hardware security architectures and tools that protect electronic systems against common classes of hardware vulnerabilities exploited through software, with the goal of breaking the endless cycle of software patch-and-pray.
To date, research on the program has focused on developing approaches an
DARPA's System Security Integration Through Hardware and firmware (SSITH) program is exploring hardware security architectures and tools that protect electronic systems against common classes of hardware vulnerabilities exploited through software, with the goal of breaking the endless cycle of software patch-and-pray.
To date, research on the program has focused on developing approaches an North Korea accuses US of 'double standards' over SLBM test
Friday, 22 October 2021 10:48 North Korea accused the United States of "double standards" over weapons testing, state media reported Thursday after an emergency UN Security Council meeting on the issue.
Pyongyang fired a new type of submarine-launched ballistic missile (SLBM) on Tuesday, the latest in a series of tests in recent weeks, prompting the US and Britain to call the diplomatic meeting in New York.
But a spo
North Korea accused the United States of "double standards" over weapons testing, state media reported Thursday after an emergency UN Security Council meeting on the issue.
Pyongyang fired a new type of submarine-launched ballistic missile (SLBM) on Tuesday, the latest in a series of tests in recent weeks, prompting the US and Britain to call the diplomatic meeting in New York.
But a spo US to curb hacking tool exports to Russia, China
Friday, 22 October 2021 10:48 US authorities unveiled Wednesday long-delayed new rules aimed at clamping down on export to nations like Russia and China of hacking technology amid a sharp uptick in cyberattacks globally.
The rules, which are set to go into force in 90 days, would prevent the sale of certain software or devices to a list of countries unless approved by a bureau of the Commerce Department.
"The United
US authorities unveiled Wednesday long-delayed new rules aimed at clamping down on export to nations like Russia and China of hacking technology amid a sharp uptick in cyberattacks globally.
The rules, which are set to go into force in 90 days, would prevent the sale of certain software or devices to a list of countries unless approved by a bureau of the Commerce Department.
"The United Permafrost thaw could release bacteria and viruses
Friday, 22 October 2021 10:47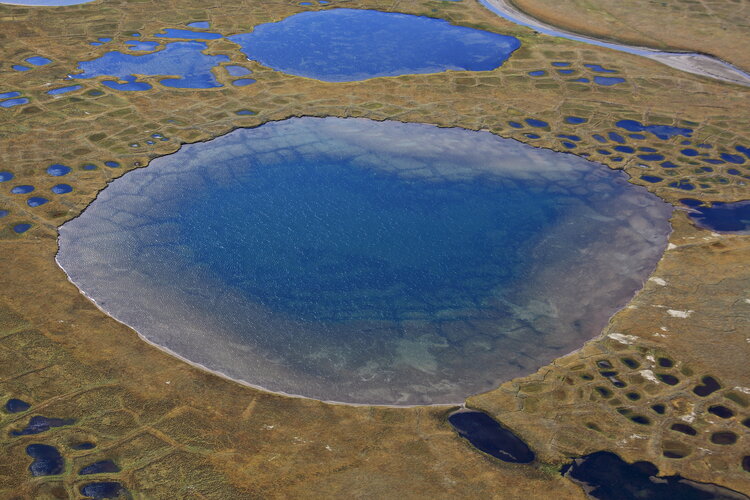
When considering the implications of thawing permafrost, our initial worries are likely to turn to the major issue of methane being released into the atmosphere and exacerbating global warming or issues for local communities as the ground and infrastructure become unstable. While this is bad enough, new research reveals that the potential effects of permafrost thaw could also pose serious health threats.
As part of the ESA–NASA Arctic Methane and Permafrost Challenge, new research has revealed that rapidly thawing permafrost in the Arctic has the potential to release antibiotic-resistant bacteria, undiscovered viruses and even radioactive waste from Cold War nuclear
