Copernical Team
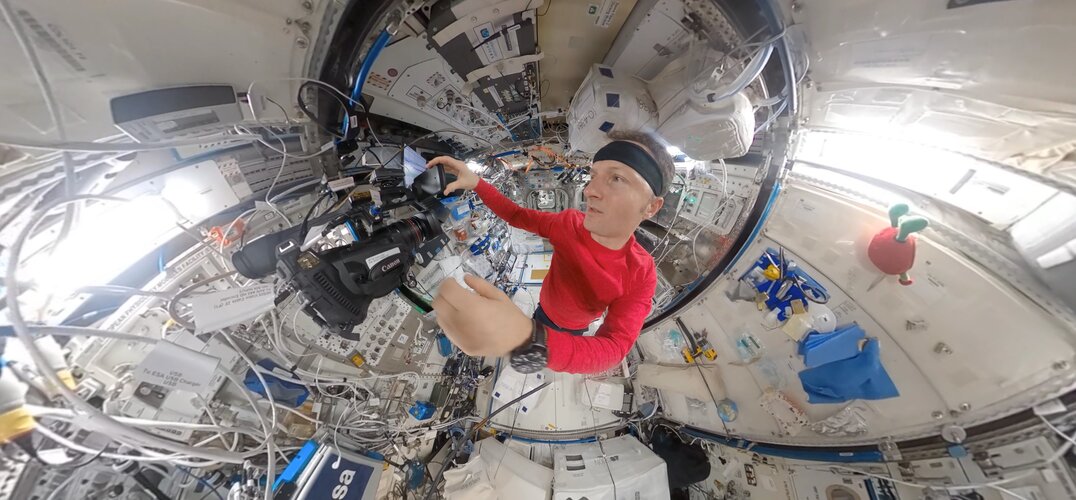
Space repairs in 360° | Cosmic Kiss
 Video:
00:01:25
Video:
00:01:25
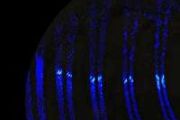
Scientist, engineer, test subject and tradesperson – astronauts in orbit wear many different hats. In this 360° timelapse, ESA astronaut Matthias Maurer works to repair a faulty valve behind EXPRESS-Rack 3.
Water On-Off Valve 8 (WOOV-8), along with WOOV-6 and WOOV-7, determines whether the cooling water of Europe’s Columbus module flows through, or bypasses, the heat exchange system that transfers waste heat to downstream cooling circuits outside the International Space Station. The valve has been a problem child for ground teams and astronauts for the past few years and was first replaced during a complicated operation in 2013.
New research strengthens link between glaciers and Earth's 'Great Unconformity'
 January 25, 2022 - New research provides further evidence that rocks representing up to a billion years of geological time were carved away by ancient glaciers during the planet's "Snowball Earth" period, according to a study published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The research presents the latest findings in a debate over what caused the Earth's "Great Unconformity"-
January 25, 2022 - New research provides further evidence that rocks representing up to a billion years of geological time were carved away by ancient glaciers during the planet's "Snowball Earth" period, according to a study published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The research presents the latest findings in a debate over what caused the Earth's "Great Unconformity"- Ancient ice reveals mysterious solar storm
 Through analyzes of ice cores from Greenland and Antarctica, a research team led by Lund University in Sweden has found evidence of an extreme solar storm that occurred about 9,200 years ago. What puzzles the researchers is that the storm took place during one of the sun's more quiet phases - during which it is generally believed our planet is less exposed to such events.
The sun is a prer
Through analyzes of ice cores from Greenland and Antarctica, a research team led by Lund University in Sweden has found evidence of an extreme solar storm that occurred about 9,200 years ago. What puzzles the researchers is that the storm took place during one of the sun's more quiet phases - during which it is generally believed our planet is less exposed to such events.
The sun is a prer Animal genomes: Chromosomes almost unchanged for over 600 million years
 Animal diversity is fascinating, but how is this reflected in their genetic material, the genome? Is it possible to definitely distinguish animals from one another based on genetic information, and perhaps even make predictions about how genetic information changes over time? This has been the great hope since the beginning of the "genome era" in 2000, when the human genome was sequenced for the
Animal diversity is fascinating, but how is this reflected in their genetic material, the genome? Is it possible to definitely distinguish animals from one another based on genetic information, and perhaps even make predictions about how genetic information changes over time? This has been the great hope since the beginning of the "genome era" in 2000, when the human genome was sequenced for the Sols 3374-3375: MAHLI Lets the Dog Out at the Prow!
 In our weekend drive we aimed to get up close to the "Toron" block, which is a "float rock" or out of place chunk of bedrock in the workspace. Unlike many float rocks, Toron's original location (tantalizingly out of reach on "The Prow,") can be pinpointed with confidence, which allows us to analyze the upper reaches of The Prow from a safe position.
The rover planners placed the rover in t
In our weekend drive we aimed to get up close to the "Toron" block, which is a "float rock" or out of place chunk of bedrock in the workspace. Unlike many float rocks, Toron's original location (tantalizingly out of reach on "The Prow,") can be pinpointed with confidence, which allows us to analyze the upper reaches of The Prow from a safe position.
The rover planners placed the rover in t Northrop Grumman to Develop Prototype Artificial Intelligence Assistant
 Northrop Grumman Corporation has been awarded a contract from the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency's (DARPA) Perceptually-enabled Task Guidance (PTG) program to develop a prototype artificial intelligence (AI) assistant. The prototype will be embedded in an augmented reality (AR) headset to help rotary pilots perform expected and unexpected tasks.
Northrop Grumman, in partnership
Northrop Grumman Corporation has been awarded a contract from the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency's (DARPA) Perceptually-enabled Task Guidance (PTG) program to develop a prototype artificial intelligence (AI) assistant. The prototype will be embedded in an augmented reality (AR) headset to help rotary pilots perform expected and unexpected tasks.
Northrop Grumman, in partnership Tech company unveils revolutionary, no-code solution to access satellite data
 In partnership with Google, in a widely attender Google Earth Outreach webinar, Earth Blox demonstrated its ability to provide near-instantaneous cloud powered access and analysis of satellite imagery in a no-code user interface (UI), opening access to Earth observation (EO) data to non-experts of every sector like never before.
Launched in 2019, Earth Blox seeks to make "EO data accessibl
In partnership with Google, in a widely attender Google Earth Outreach webinar, Earth Blox demonstrated its ability to provide near-instantaneous cloud powered access and analysis of satellite imagery in a no-code user interface (UI), opening access to Earth observation (EO) data to non-experts of every sector like never before.
Launched in 2019, Earth Blox seeks to make "EO data accessibl Atlanta to host key SMR and Advanced Reactor event in May
 Nuclear power's role in cutting carbon emissions will be a major topic at SMR and Advanced Reactor 2022 in Atlanta, Reuters Events announced today.
The world's foremost event for advanced and small modular reactors (SMRs) will take place in the Georgia state capital on May 24 and 25, bringing together more than 500 experts together in a sector that could be key in the global fight against
Nuclear power's role in cutting carbon emissions will be a major topic at SMR and Advanced Reactor 2022 in Atlanta, Reuters Events announced today.
The world's foremost event for advanced and small modular reactors (SMRs) will take place in the Georgia state capital on May 24 and 25, bringing together more than 500 experts together in a sector that could be key in the global fight against Weightless placozoa - how gravity influences genetic information
 Usually, placozoa prefer warmer temperatures. For science, the simplest multicellular organisms in the world have made its way to northern Sweden - and from there into microgravity for a short time. On board the German Aerospace Center (Deutsches Zentrum fur Luft- und Raumfahrt; DLR) MAPHEUS 9 sounding rocket, the marine organisms successfully launched from the Esrange Space Center rocket launch
Usually, placozoa prefer warmer temperatures. For science, the simplest multicellular organisms in the world have made its way to northern Sweden - and from there into microgravity for a short time. On board the German Aerospace Center (Deutsches Zentrum fur Luft- und Raumfahrt; DLR) MAPHEUS 9 sounding rocket, the marine organisms successfully launched from the Esrange Space Center rocket launch New theory about mysterious location of massive stars
 Astronomers from Georgia State University have found an explanation for the strange occurrence of massive stars located far from their birthplace in the disk of our Milky Way Galaxy.
Stars more massive than the Sun have very hot cores that drive nuclear energy generation at very high rates. They are among the brightest objects in our galaxy. But because they burn through their hydrogen fue
Astronomers from Georgia State University have found an explanation for the strange occurrence of massive stars located far from their birthplace in the disk of our Milky Way Galaxy.
Stars more massive than the Sun have very hot cores that drive nuclear energy generation at very high rates. They are among the brightest objects in our galaxy. But because they burn through their hydrogen fue