Displaying items by tag: laboratory
Laboratoire d'Astrophysique de Bordeaux (LAB)
The Laboratory of Astrophysics of Bordeaux (LAB) is a French research centre.
It is a joint research unit of CNRS and the University Bordeaux 1 Science and Technology. It is an integral part of the Aquitanian Observatory for the Sciences of the Universe.
The main missions are :
- international research in the fields of astronomy and astrophysics
- basic and continuing training
- public outreach
The laboratory is composed of researchers and teacher-researchers, engineers, technicians and administrative staff, PhD students and post-docs.
Space Dynamics Laboratory, Utah Univ.
The Space Dynamics Laboratory (SDL) is a not-for-profit unit of the Utah State University Research Foundation.
SDL's mission is to solve technical challenges faced by the military, science community, and industry through:
- Serving MDA and the DoD as the University Affiliated Research Center (UARC) for electro-optical sensor systems research and development.
- Designing and delivering electro-optical and space environment sensors and subsystems for over 400 rocket-borne and space-based payloads.
- Pioneering efficient and effective calibration and characterization techniques and facilities.
- Innovating CubeSat busses and small-scale components that provide large-scale benefits to the customer.
- Enabling significant advances in data compression, processing, and exploitation.
- Developing real-time reconnaissance data visualization hardware and software for operational military applications.
Tiangong 1
Tiangong-1 is China's first space laboratory module, an experimental testbed to demonstrate the rendezvous and docking capabilities needed to support a space station complex. Launched unmanned aboard a Long March 2F/G rocket on 29 September 2011, it is part of the Tiangong program, which aims to place a larger, modular station into orbit by 2020. Tiangong-1 will be deorbited in 2013, and replaced over the following decade by the larger Tiangong-2 and Tiangong-3 modules.
Tiangong-1 will be visited by a series of Shenzhou spacecraft during its two-year operational lifetime. The first of these, the unmanned Shenzhou 8, successfully docked with the module in November 2011; the manned Shenzhou 9 mission is expected to launch to Tiangong-1 in June 2012.
INTEGRAL
INTEGRAL is the first space observatory that can simultaneously observe objects in gamma rays, X-rays and visible light.
The European Space Agency's INTErnational Gamma-Ray Astrophysics Laboratory (INTEGRAL) is an operational Earth satellite, launched in 2002 for detecting some of the most energetic radiation that comes from space. It is the most sensitive gamma ray observatory ever launched.
INTEGRAL is an ESA mission in cooperation with the Russian Space Agency and NASA. It has had some notable successes, for example in detecting a mysterious 'iron quasar'. It has also had great success in investigating gamma-ray bursters and evidence for black holes.
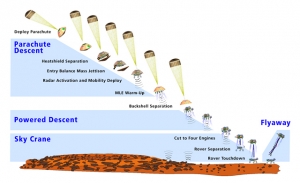
The MSL mission (Mars Science Laboratory)
The Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) is a National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) mission with the aim to land and operate a rover named Curiosity on the surface of Mars.
The MSL was launched November 26, 2011 at 10:02 am EST and will land on Mars at Gale Craterbetween August 6 and August 20, 2012. It will attempt to perform the first-ever precision landing on Mars. The rover Curiosity will help assess Mars' habitability, that is, whether Mars is, or ever was an environment able to support microbial life. It will also analyze samples scooped up from the soil and drilled powders from rocks.