Displaying items by tag: altimetry
Copernicus: Sentinel-3 - Global Sea/Land Monitoring Mission including Altimetry
The Sentinel-3 (S3) mission of ESA and the EC is one of the elements of the GMES (Global Monitoring for Environment and Security) program, which responds to the requirements for operational and near-real-time monitoring of ocean, land and ice surfaces over a period of 20 years. The topography element of this mission will serve primarily the marine operational users but will also allow the monitoring of sea ice and land ice, as well as inland water surfaces, using novel observation techniques.The Sentinel-3 mission is designed as a constellation of two identical polar orbiting satellites, separated by 180º, for the provision of long-term operational marine and land monitoring services. The operational character of this mission implies a high level of availability of the data products and fast delivery time, which have been important design drivers for the mission. 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) 9) 10) 11) 12) 13) 14)
The Sentinel-3 program represents a series of operational spacecraft over the envisioned service period to guarantee access to an uninterrupted flow of robust global data products.
Geoscience Laser Altimeter System (GLAS)
The Geoscience Laser Altimeter System (GLAS) is an instrument onboard the ICESat satellite.
This instrument will determine the distance from the satellite to the Earth's surface and to intervening clouds and aerosols. It will do this by precisely measuring the time it takes for a short pulse of laser light to travel to the reflecting object and return to the satellite. Although surveyors routinely use laser methods, the challenge for ICESat is to perform the measurement 40 times a second from a platform moving 26,000 km (16,000 mi) per hour. In addition, ICESat will be 600 km above the Earth and the precise locations of the satellite in space and the laser beam on the surface below must be determined at the same time.
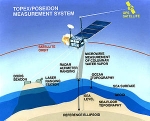
TOPEX/Poseidon satellite
Launched on August 10, 1992, TOPEX/Poseidon was a joint satellite mission between NASA, the U.S. space agency, and CNES, the French space agency, to map ocean surface topography. The first major oceanographic research vessel to sail into space, TOPEX/Poseidon helped revolutionize oceanography by proving the value of satellite ocean observations.
The satellite operations ended on January 2006.
Jason-1 was launched in 2001 to continue the on-going measurements of sea surface topography.