Displaying items by tag: Boeing
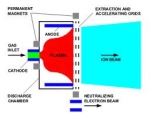
XIPS - Xenon Ion Propulsion System
XIPS is a com-mercial electron bom-bardment thruster (also known as an electrostatic ion thruster) – a form ion propulsion – that is a product of Hughes Space and Communications Company, which, in 2000, became part of Boeing Satellite Systems.
XIPS (pronounced "zips") employs the heavy inert gas xenon as a propellant. It was first used operationally aboard the PAS-5 (PanAmSat-5) communications satellite in 1997 and has since been fitted to many other geosynchronous satellites for use primarily in station-keeping. In a XIPS, xenon atoms are injected into an ionization chamber and ionized by electron bombardment. The propellant is then electrostatically accelerated through a series of biased grids. Ions, ejected by XIPS, travel in a stream at a speed of 30 km/s (62,900 mph), nearly 10 times that of a conventional chemical thruster. The high efficiency of the system leads to a reduction in propellant mass of up to 90% for a satellite designed for 12–15 years operation.
For example on a XIPS equipped Boeing 702 satellite, four 25-cm thrusters provide economical station keeping, needing only 5 kg of fuel per year. Boeing asserts that this is "a fraction of what bipropellant or arcjet systems consume". Boeing further asserts, that a XIPS can be used for final orbit insertion and has orders ( source: Wikipedia, Boeing_702 ) for spacecraft utilizing only ion thrusters. This conserves even more payload mass, as compared to using an on-board liquid apogee engine.
Boeing 702 satellite
The Boeing 702 satellite is a family of geostationnary satellites designed and manufactured by the company Boeing.
Its design requirements include lower cost and high reliability. It offers a broad spectrum of modularity. A primary example is payload/bus integration. After the payload is tailored to customer specifications, the payload module mounts to the common bus module at only four locations and with only six electrical connectors. This design simplicity confers advantages. First, nonrecurring program costs are reduced, because the bus does not need to be changed for every payload, and payloads can be freely tailored without affecting the bus. Second, the design permits faster parallel bus and payload processing. This leads to the third advantage: a short production schedule.
Further efficiency derives from the 702's advanced xenon ion propulsion system (XIPS), which was pioneered by Boeing. XIPS is 10 times more efficient than conventional liquid fuel systems. Four 25-cm thrusters provide economical stationkeeping, needing only 5 kg of fuel per year - a fraction of what bipropellant or arcjet systems consume. Using XIPS for final orbit insertion conserves more mass as compared to using an on-board liquid apogee engine. Customers can apply the weight savings to increase the revenue-generating payload, to prolong service life, or to change to a less expensive launch vehicle (when cost is based on satellite mass).
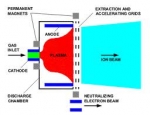
XIPS - Xenon Ion Propulsion System
XIPS is a commercial electron bombardment thruster (also known as an electrostatic ion thruster) – a form ion propulsion – that is a product of Hughes Space and Communications Company, which, in 2000, became part of Boeing Satellite Systems.
XIPS (pronounced "zips") employs the heavy inert gas xenon as a propellant. It was first used operationally aboard the PAS-5 (PanAmSat-5) communications satellite in 1997 and has since been fitted to many other geosynchronous satellites for use primarily in station-keeping. In a XIPS, xenon atoms are injected into an ionization chamber and ionized by electron bombardment. The propellant is then electrostatically accelerated through a series of biased grids. Ions, ejected by XIPS, travel in a stream at a speed of 30 km/s (62,900 mph), nearly 10 times that of a conventional chemical thruster. The high efficiency of the system leads to a reduction in propellant mass of up to 90% for a satellite designed for 12–15 years operation.
For example on a XIPS equipped Boeing 702 satellite, four 25-cm thrusters provide economical station keeping, needing only 5 kg of fuel per year. Boeing asserts that this is "a fraction of what bipropellant or arcjet systems consume". Boeing further asserts, that a XIPS can be used for final orbit insertion and has orders( source: Wikipedia, Boeing_702 ) for spacecraft utilizing only ion thrusters. This conserves even more payload mass, as compared to using an on-board liquid apogee engine.
Boeing 702 satellite
The Boeing 702 satellite is a family of geostationnary satellites designed and manufactured by the company Boeing.
Its design requirements include lower cost and high reliability. It offers a broad spectrum of modularity. A primary example is payload/bus integration. After the payload is tailored to customer specifications, the payload module mounts to the common bus module at only four locations and with only six electrical connectors. This design simplicity confers advantages. First, nonrecurring program costs are reduced, because the bus does not need to be changed for every payload, and payloads can be freely tailored without affecting the bus. Second, the design permits faster parallel bus and payload processing. This leads to the third advantage: a short production schedule.
Further efficiency derives from the 702's advanced xenon ion propulsion system (XIPS), which was pioneered by Boeing. XIPS is 10 times more efficient than conventional liquid fuel systems. Four 25-cm thrusters provide economical stationkeeping, needing only 5 kg of fuel per year - a fraction of what bipropellant or arcjet systems consume. Using XIPS for final orbit insertion conserves more mass as compared to using an on-board liquid apogee engine. Customers can apply the weight savings to increase the revenue-generating payload, to prolong service life, or to change to a less expensive launch vehicle (when cost is based on satellite mass).